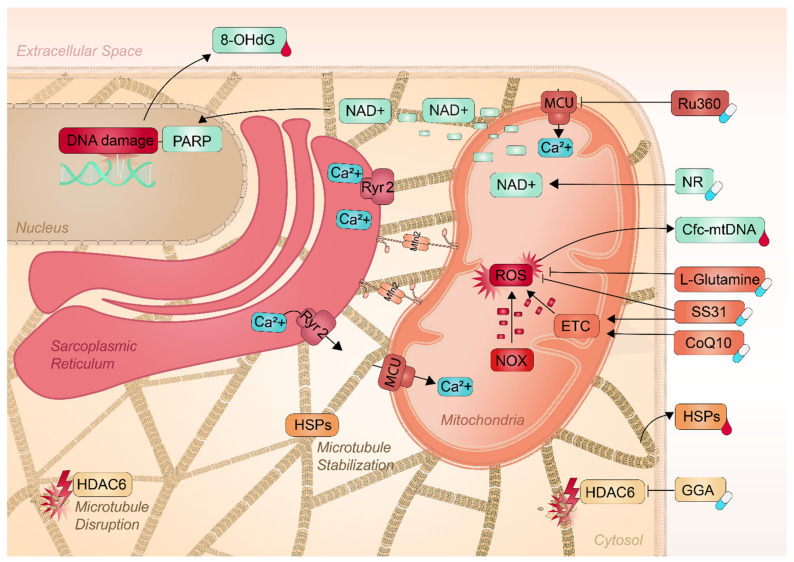
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of the pathophysiological processes during AF and the potential biomarkers and therapeutic implications. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been identified as a contributing factor in AF. Modulators of mitochondrial dysfunction such as 8-OHdG and cfc-mtDNA may aid in the staging of the severity of AF, predicting postoperative AF (POAF) onset, and the outcome of AF treatments. In addition, various pharmaceutical- and nutraceutical compounds are under investigation nowadays. Pharmaceutical compounds such as SS31, Ru360, or HSP inducer GGA and nutraceutical compounds such as NR, L-glutamine, and CoQ10 may present novel therapeutic strategies to counteract AF-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.