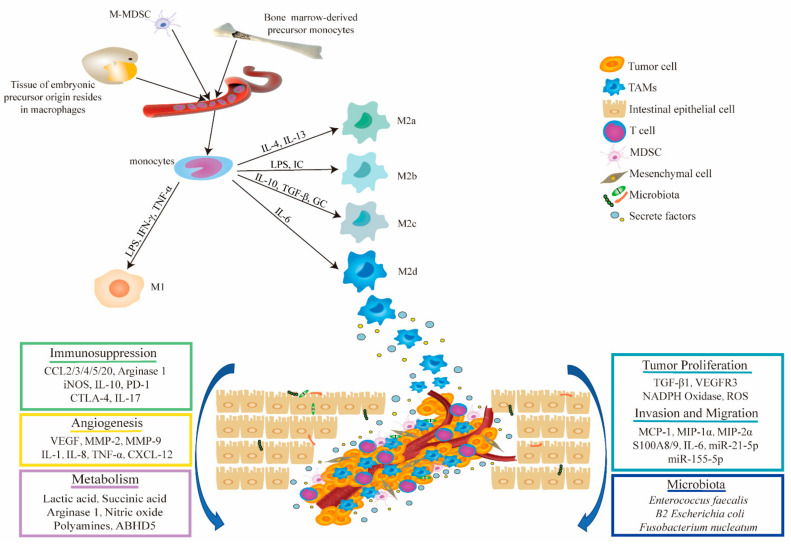
Figure 1.
Origin and phenotypic polarization of TAMs and their functional mechanism in CRC. TAMs mainly originate from monocytes which arise from bone marrow-derived precursors, tissues of embryonic precursors, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSC). TAMs can be polarized into classically activated M1 (pro-inflammatory) and alternatively activated M2 (anti-inflammatory) macrophages. TAMs promote tumor occurrence and malignant progression by stimulating tumor-related angiogenesis; promoting tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis; inhibiting the antitumor immune response; regulating metabolism; and interacting with microbiota in the GI tract. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IC, immune complex; GC, glucocorticoid. The legend for different cell types is shown in the upper right.