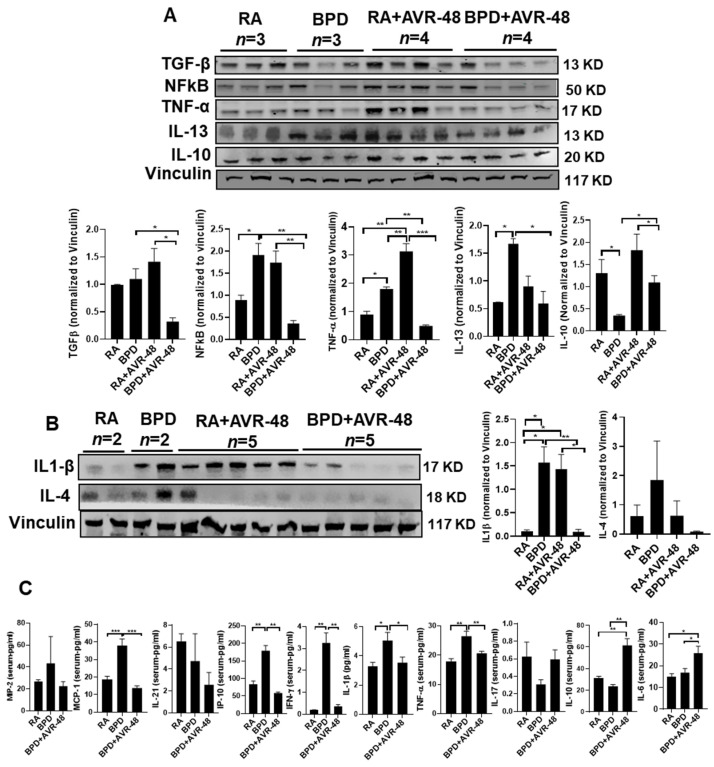
Figure 7.
AVR-48 suppresses inflammation. (A,B) Representative Western blot showing decrease of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TGFβ, NFkB, TNFα, IL-13, IL-1β, and IL-4) and increase of IL-10 in the lungs after treatment with AVR-48, as compared to the BPD group. The increased inflammation seen in the RA+AVR-48 treated group may be due to the natural defense adaptive mechanism. Vinculin is the loading control. The panel below the gel shows densitometric quantification of the proteins. n = 5. (C) ELISA showing the expression of selected cytokines in the blood serum of treated BPD group as compared to untreated BPD controls. The RA+AVR-48 group was not included for this assay. Although most of the pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines show a decrease after treatment, there was no change in MIP-2, IL-21, or IL-17. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, n = 4–5; RA: room air; BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; TGFβ: transforming growth factor beta; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; MIP-2: macrophage inflammatory protein 2; NfkB: nuclear factor kappa B; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha; IFNγ: interferon gamma; IL: interleukin.