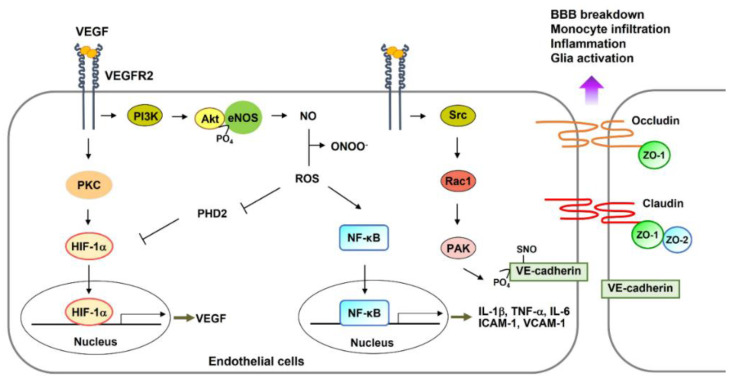
Figure 1.
Following an acute ischemic stroke, VEGF, whose expression is enhanced, binds with VEGFR2 and triggers various signaling pathways in endothelial cells. For instance, the VEGFR2–PKC pathway may activate the transcription factor of VEGF and HIF-1α. Next, the PI3K–Akt pathway phosphorylates eNOS and activates eNOS enzymatic functions leading to NO production. Oxidative stress mediates ROS production. ROS reacts with NO to synthesize peroxynitrite (ONOO−). ROS signaling inhibits PHD2 activity, leading to HIF-1a protein stabilization and activation of NF-κB protein, consequently upregulating expression of downstream genes related to NF-κB, such as IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1. ONOO− modifies VE-cadherin protein by nitrosylation of serine residues, resulting in the detachment of VE-cadherin from endothelial cells. Finally, the VEGFR2-mediated Src–Rac1–PAK pathway phosphorylates VE-cadherin, resulting in dissociation with the adherence junction between endothelial cells. Oxidative stress-mediated reduction in the expression of tight junction proteins also initiates BBB breakdown and monocyte infiltration. HIF-1α- and NF-κB-mediated gene expression facilitates BBB breakdown, inflammatory responses, and glial scarring. Abbreviations: VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; NO, nitric oxide; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; HIF-1α, hypoxia-induced factor-1α; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PAK, p21-activated kinase; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial cadherin; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; ZO, zonula occludens; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PHD, prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain; BBB, blood–brain barrier.