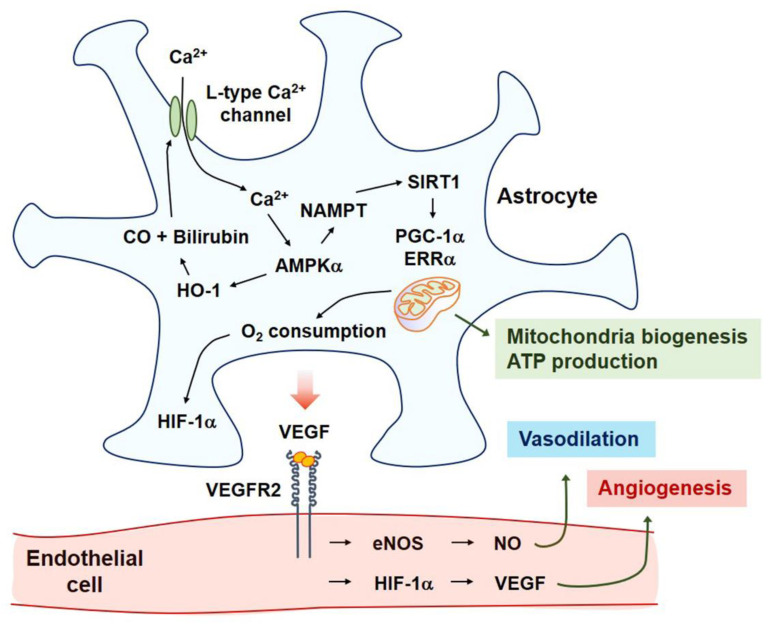
Figure 2.
After the ischemia-reperfusion injury, HO-1 is expressed in the astrocytes of the penumbra of the ischemic brain. CO and bilirubin can be produced via enzymatic activity of HO-1, which then activates the L-type Ca2+ channel, leading to the entry of extracellular Ca2+. Ca2+-mediated AMPKα-HO-1 circuit results in NAMPT gene expression and consequent SIRT1 activation. Deacetylation of PGC-1α by SIRT1 activates ERRα expression. PGC-1α-ERRα axis induces mitochondrial biogenesis, ATP production, and increased O2 consumption. Reduction of O2 inhibits PHD2 activity and then stabilizes HIF-1α protein. Both the PGC-1α-ERRα pathway and HIF-1α pathway induce the expression and secretion of VEGF. VEGF dimerization and binding to VEGFR2 triggers the eNOS–NO axis and HIF-1α–VEGF pathway in endothelial cells, leading to vasodilation and angiogenesis, respectively. Abbreviations: CO, carbon monoxide; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; AMPKα, AMP-activated protein kinase α; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-coactivator-1α; PHD, prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain; ERRα, estrogen-related receptor α; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase.