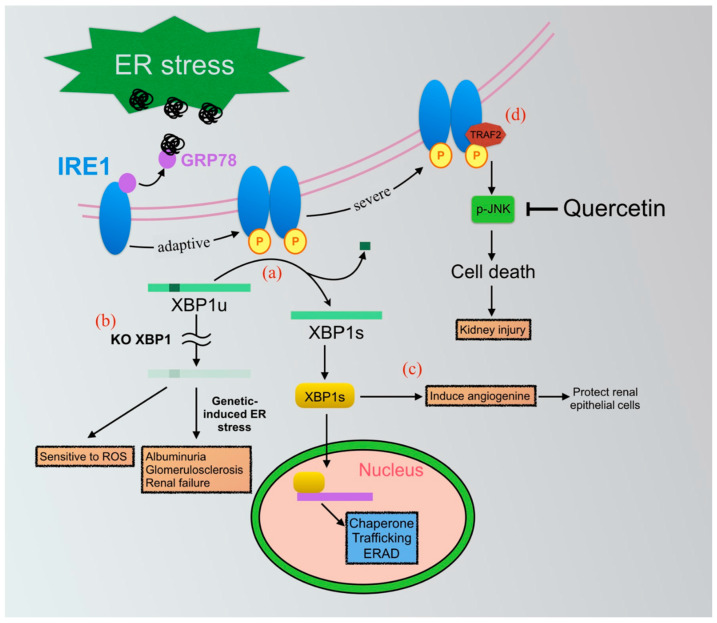
Figure 1.
The IRE1-XBP1-related UPRs pathways played pathological and therapeutic roles in kidney disease. (a) Unfolded proteins bind to BiP and allow the activation of IRE1 to occur through its dimerization and trans-autophosphorylation. IRE1 phosphorylation as indicated p in the yellow cycle. Activated IRE1 splices the mRNA of XBP1u to form spliced XBP1 (XBP1s) mRNA, which encodes XBP1s protein then translocates to the nucleus, inducing genes that are thought to be generally cytoprotective, such as chaperones, trafficking associators, ERAD-related proteins. (b) Evidence shows that XBP1 knockout makes cells sensitive to oxidative stress, an important insult to kidney injury. Combining the XBP1 knockout model with genetically induced ER stress in the kidney leads to severe albuminuria, glomerulosclerosis, and renal failure. (c) XBP1s could directly induce angiogenin (ANG) expression in renal epithelial cells, which has been proven to protect cells and attenuate adverse effects caused by ER stress. (d) Severe ER stress triggers cell death through the IRE1-TRAF2-JNK pathway in many kinds of kidney diseases. Quercetin, a natural flavonoid, has been demonstrated to inhibit the IRE1-TRAF2-JNK pathway in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO), diabetic nephropathy, and cadmium-induced kidney injury. It might be a strong therapeutic option for the targeting of UPRs.