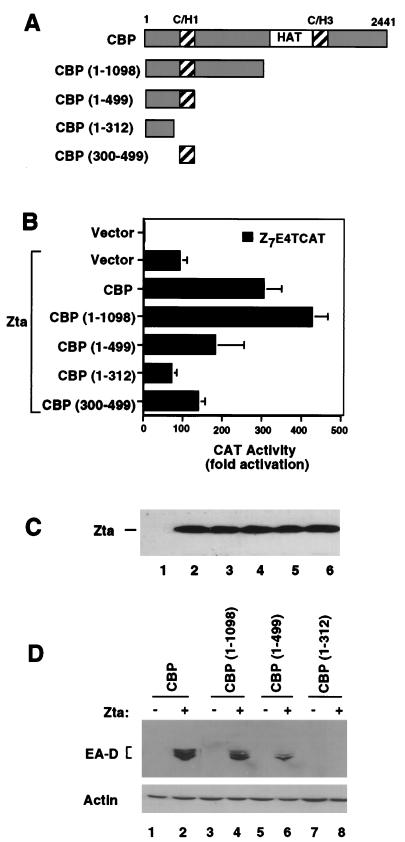
FIG. 6.
The amino-terminal C/H1 domain of CBP is required for coactivation with Zta. (A) Schematic of CBP deletion mutants used to map the amino-terminal coactivation function of CBP. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with Z7E4TCAT (1 μg) and either pRTS2 vector (1 μg) or Zta expression plasmid (1 μg). Expression plasmids for full-length CBP or the amino-terminal fragments CBP (1–1098), CBP (1–499), CBP (1–312), or CBP (300–499) were cotransfected (4 μg of each) and assayed for CAT activity 48 h posttransfection. CAT activity is reported as fold activation above that for vector alone. (C) Extracts derived from transfected HeLa cells described in panel B were assayed for levels of Zta expression by Western blot analysis. Zta is expressed in all samples except lane 1. Levels of Zta were measured when cotransfected with pRTS2 vector (lane 2), full-length CBP (lane 3), CBP (1–1098) (lane 4), CBP (1–499) (lane 5), and CBP (1–312) (lane 6). (D) D98/HR1 cells were assayed for the ability of CBP N-terminal fragments to stimulate EA-D expression. The cells were transfected with 1 μg of Zta expression plasmid (+) or pRTS2 vector (−) and cotransfected with 4 μg of either CBP, CBP (1–1098), CBP(1–499), or CBP (1–312) as indicated above the lanes. The cells were analyzed by Western blotting 48 h posttransfection for the expression of EA-D (top) or for actin (bottom).