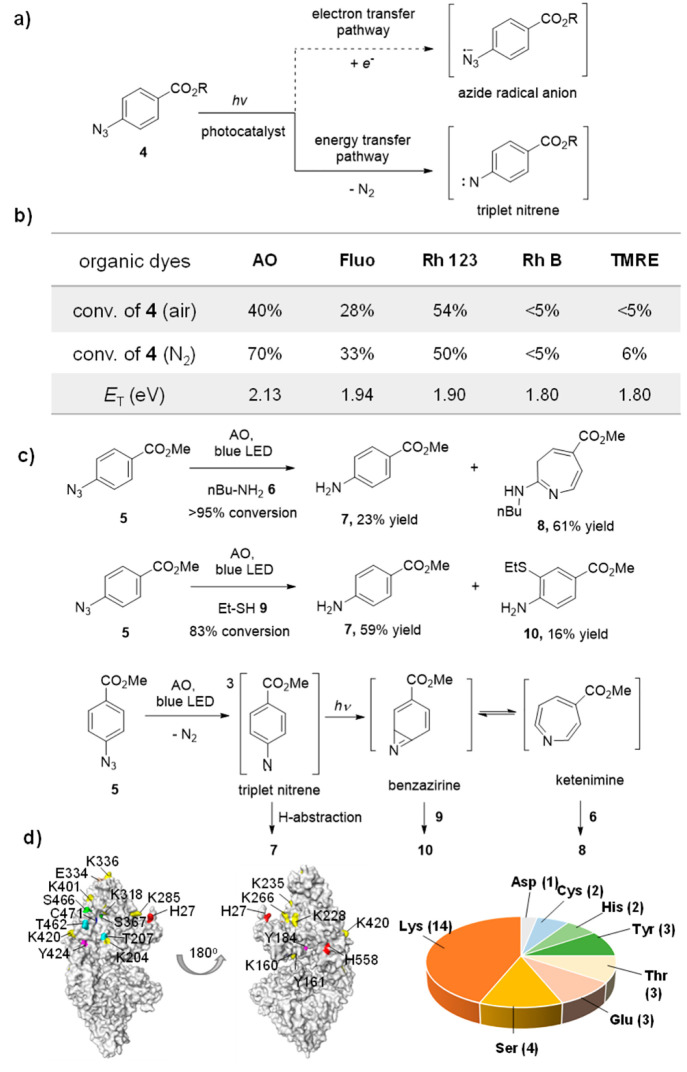
Figure 3.
Mechanistic studies of the photocatalytic azide-promoted protein labeling reaction. (a) Plausible photocatalysis reaction pathways (single electron transfer or energy transfer) to generate the reactive intermediates from aryl azides. (b) Conversion of 4-azidobenzoic acid 4 (R = H) (200 μM) after visible light irradiation at 25 °C for 1 h in PBS buffer (10 mM, pH 7.4) (xenon lamp equipped with band-pass filters, 19.8 mW cm–2) by organic dyes (50 μM) with different triplet energies. c) The formation of aniline 7, azepine 8, and thiolether-substituted aniline 10 supported the triplet nitrene, ketenimine, and benzazirine intermediates. The solution of 5 (0.10 mmol), Acridine Orange (0.020 mmol) and amine or thiols (5 mmol) in methanol were under blue LED (10.4 mW/cm2) irradiation at 25 °C for 40–48 h. (d) LC-MS/MS analysis of the AzPh-biotin probe 1 labeled nucleophilic amino acid residues on BSA protein. The identified sites are partially labeled on the crystal structure of BSA, and the whole identified sites are shown in Figure S28.