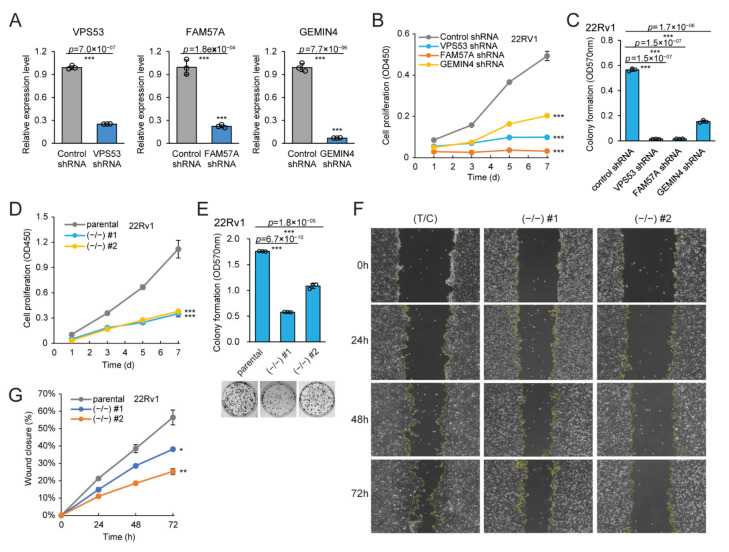
Figure 6.
VPS53, FAM57A, and GEMIN4 knockdown impede cancerous phenotypes. (A) Effect evaluation of lentiviral shRNAs targeting VPS53, FAM57A, and GEMIN4 in 22Rv1 cells. Mean ± SD of three technical replicates. *** p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (B) Cell proliferation assay of 22Rv1 cells undergoing lentiviral shRNA gene knockdown targeting VPS53, FAM57A, and GEMIN4, respectively. Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 method at 1–7 d post-seeding. Mean ± SD of three biological replicates. *** p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (C) Colony formation assay of 22Rv1 cells undergoing lentiviral shRNA gene knockdown targeting VPS53, FAM57A, and GEMIN4. Cell colonies were quantified through the Crystal Violet staining method. Mean ± SD of three biological replicates. *** p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (D) Cell proliferation assay for the two genome-edited 22Rv1 cells with rs684232 site mutated through indels. Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 method at 1–7 d post-seeding. Mean ± SD of three biological replicates. *** p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (E) Colony formation assay for the two genome-edited 22Rv1 cells. Cell colonies were quantified through the Crystal Violet staining method. Representative images from triplicate experiments on the bottom. Mean ± SD of three biological replicates. *** p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (F) Wound healing assay of the two rs684232 knockout 22Rv1 cell lines. Representative images from triplicate experiments. (G) The wound closure percentages in the wound healing assay experiments were quantified using Image J software. Mean ± SEM of three biological replicates. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-test.