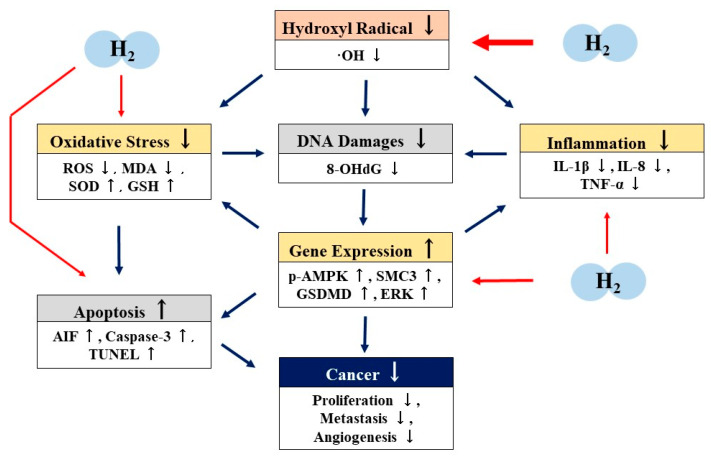
Figure 2.
Possible mechanism of the antitumor effects of molecular hydrogen (H2.) H2 scavenges hydroxyl radicals (·OH) directly. H2 also exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and apoptotic effects through the regulation of gene expression indirectly. Through these direct and indirect actions, H2 may exhibit antitumor effects. H2: molecular hydrogen; ·OH: hydroxyl radicals; ROS: reactive oxygen species; MDA: malondialdehyde; SOD: superoxide dismutase; GSH: glutathione; 8-OHdG: 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanidine; p-AMPK: phosphorylated adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; AIF: apoptosis-inducing factor; TUNEL: TdT-mediated digoxygenin (biotin)-dUTP nick end labeling; SDMD: gasdermin D; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-8: iterleukin-8; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor-α.