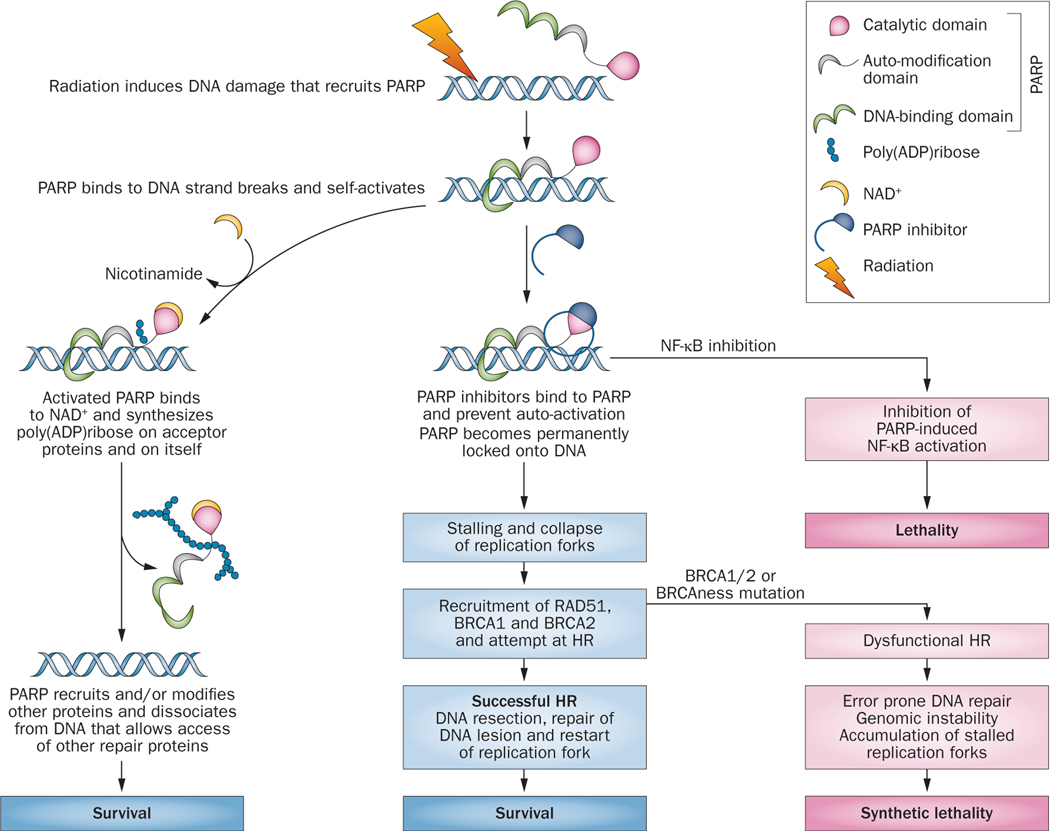
Figure 2 |.
Possible mechanisms by which PARP-1 inhibitors might interact with radiation-induced DNA damage for therapeutic benefit. PARP inhibitors cause synthetic lethality in cells that have a compromised HR apparatus or can block cell survival pathways activated through NF-κB. On the left of the diagram, once PARP disassociates from the DNA complex, recruitment of repair proteins XRCC1 and DNA ligase III for repair of SSBs by BER commences; MRE11 and ATM facilitate DSB repair through HR. MRE11 also facilitates restart of stalled replication forks. The repair proteins help regulate chromatin structure, DNA methylation, histone H1 binding to chromatin, and transcriptional regulation of survival genes, such as NF-kB. Abbreviations: BER, base-excision repair; CD, C-terminal catalytic domain; DSB, double-strand break; HR, homologous recombination; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; SSBs, single-strand breaks; PARP, poly(ADPribose) polymerase.