Fig. 2. Transfer assays to study cell-cell communication by EVs.
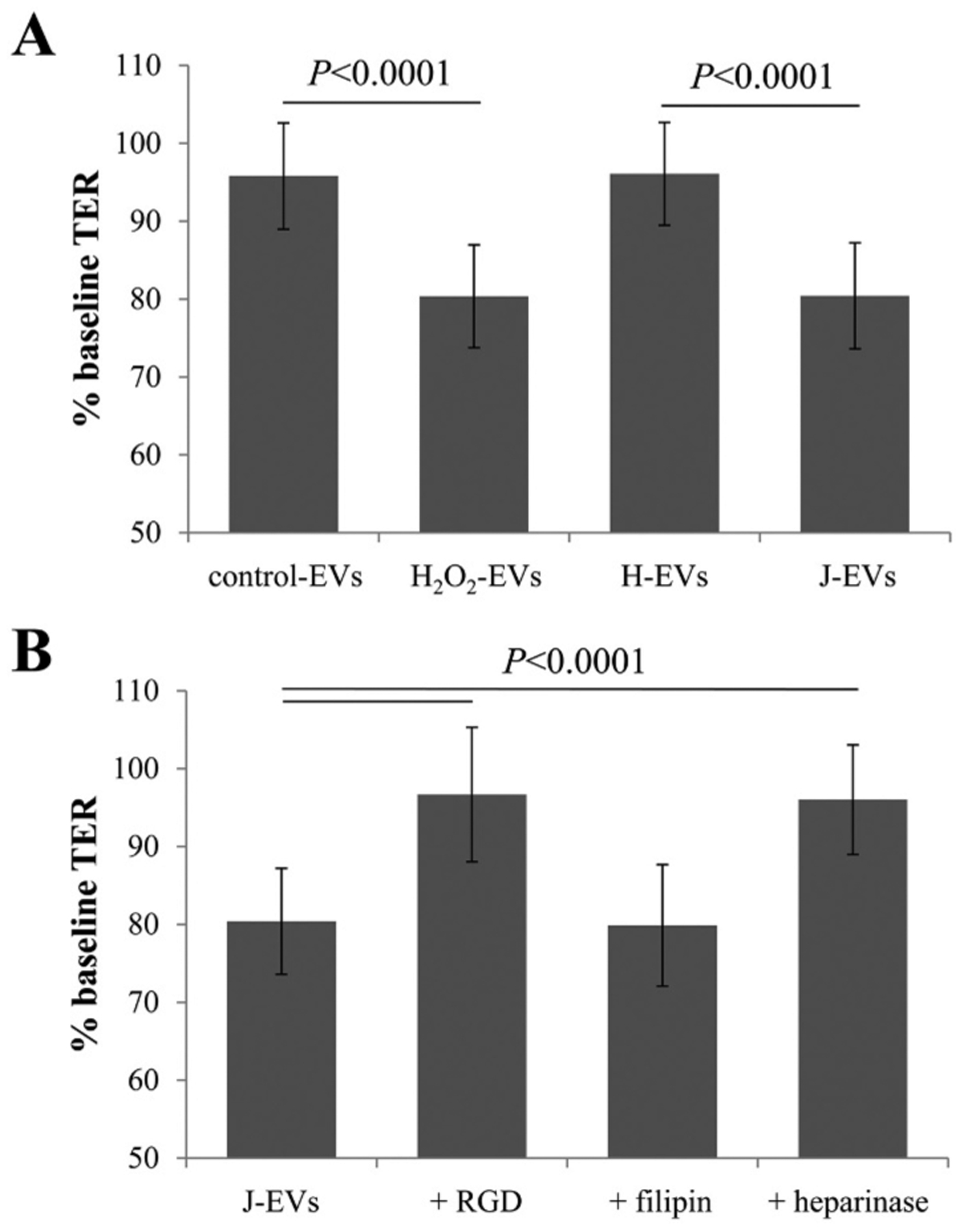
Transepithelial resistance (TER) assays are used to study bystander effects elicited by EV transfer as published, comparing TER measurements between 0 (baseline) and 4 h time point (post treatment). A reduction in TER is understood as successful uptake of EVs by recipient cells [20]. (A) EVs from ARPE-19 cell monolayers (donor cells) of control or stressed (H2O2) were transferred directly to the apical side of naïve monolayers (recipient cells). EVs from stressed cells reduced TER as reported [20]. EVs from H-cybrids (H EVs) behaved like control EVs, whereas J-cybrids (J EVs) behaved like H2O2 EVs. (B) Pretreatment of recipient cells with RGD peptide (integrin receptor inhibitor) or heparinase (removes surface proteoglycans) prevented TER reduction induced by J EVs, whereas pretreatment of EVs with filipin (inhibits lipid-based interaction) did not. Bar graphs represent mean ± stdev (n = 30–35). Significance was obtained using a posthoc ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.
