Fig. 3.
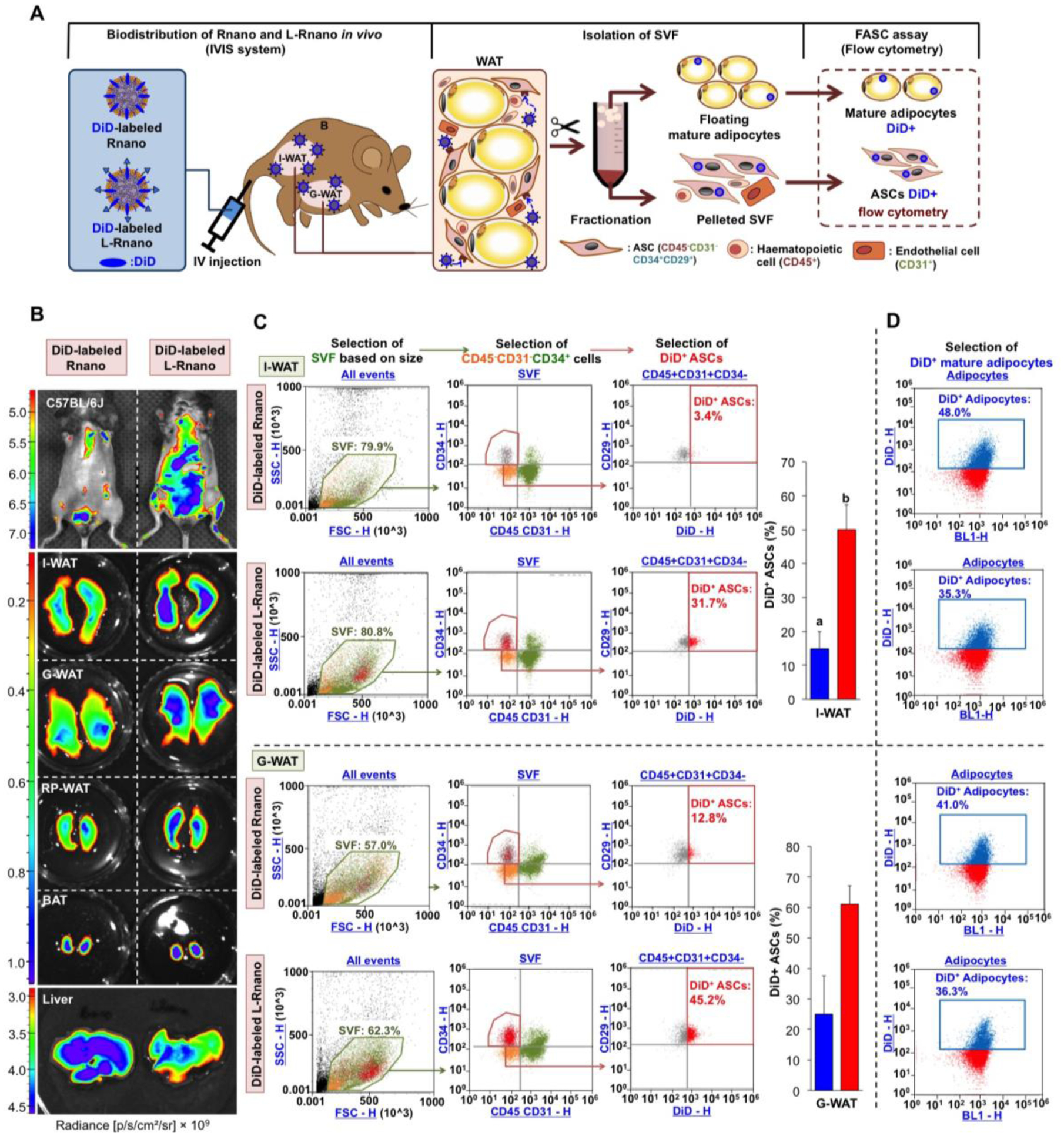
L-Rnano target WAT-derived ASCs in C57BL/6J mice. (A) Schematic of intravenous administration of Rnano and L-Rnano, SVF isolation, ASC identification, and quantification of DiD+ ASCs and mature adipocytes. (B) IVIS images of mice, WAT depots, BAT and the liver after 24-hour post intravenous administration of DiD-labeled Rnano or L-Rnano. Radiance (p/s/cm2/sr) is shown. Images are representatives of three independent experiments. (C) Binding and uptake of DiD-labeled Rnano or L-Rnano by ASCs in I-WAT or G-WAT was measured by flow cytometry. (D) Binding and uptake of DiD-labeled Rnano or L-Rnano by mature white adipocytes isolated from the I-WAT or G-WAT. Bars without a common superscript differ, p<0.05 by a two-tailed Student’s t-test.
