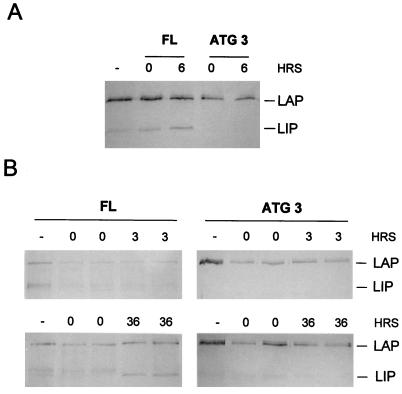
FIG. 9.
Induction of LIP during liver regeneration occurs by a translational mechanism. (A) In vitro translation of C/EBPβ in the absence (−) or presence of cytoplasmic extracts (CE) from regenerating rat livers. Extracts were added from rat livers at 0 or 6 h (HRS) after PH (times indicated above the gel). The left three lanes contain C/EBPβ translated from the wild-type C/EBPβ construct (FL), and the right two lanes contain C/EBPβ translated from the LIP mutant construct (ATG 3). The positions of LAP and LIP are indicated at the right. (B) In vitro translation of C/EBPβ in the presence of CE from regenerating mouse livers. Extracts were added from mouse livers at 0, 3, or 36 h after PH (times indicated above the gel). CE from two different animals were used in parallel. The left column depicts the use of the wild-type C/EBPβ construct (FL), and the right column depicts the use of the LIP mutant construct (ATG 3). The positions of LAP and LIP are indicated at the right.