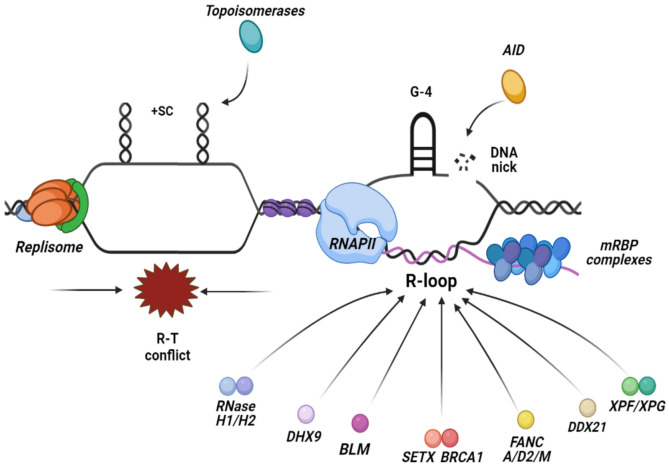
Figure 2.
R-loops are formed at the site of collisions between the replisome and RNAPII when they move along the DNA in opposite directions, leading to a head-on conflict between the two machineries. The main preventative mechanisms that inhibit R-loops accumulation are the regulation of torsional stress via the topoisomerases activity that relaxes supercoiled DNA in the vicinity of the forks and the transcript regulation, ensuring the proper packaging and processing of the mRNA. Factors implicated in the resolution of R-loops include nucleases such as, RNase H1/2 enzymes that hydrolyze the RNA moiety of the RNA:DNA hybrid and TC-NER factors, and a plethora of RNA/DNA helicases that unwind the hybrid.