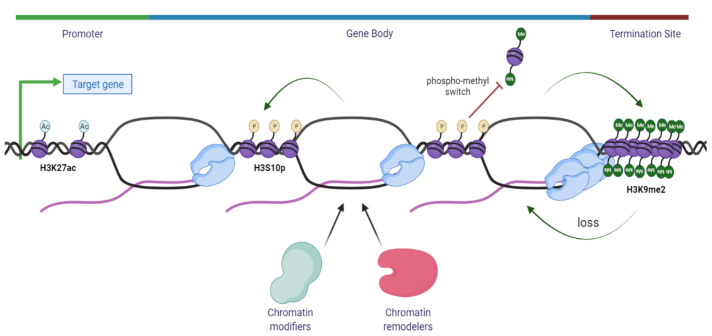
Figure 3.
Summary of chromatin modifications associated with the R-loops. R-loops accumulate at the promoter region of genes and are usually associated with an open chromatin structure characterized by H3 acetylation marks, such as H3K27ac and other permissive epigenetic modifications, allowing gene expression and transcription initiation. At terminators, R-loops are formed to induce transcription termination at sites with paused RNAPII, and these R-loops induce the activity of EHMT2/G9a methyltransferase to compact the chromatin by depositing the heterochromatin H3K9me2 mark. Moreover, R-loops are also associated with a closed chromatin architecture that induces repressive marks, such as H3S10p, that might act as a platform for chromatin modifiers and remodelers to alter the chromatin landscape. The antagonism between H3S10p and H3K9me2 prevents the spread of heterochromatin regions across the genome.