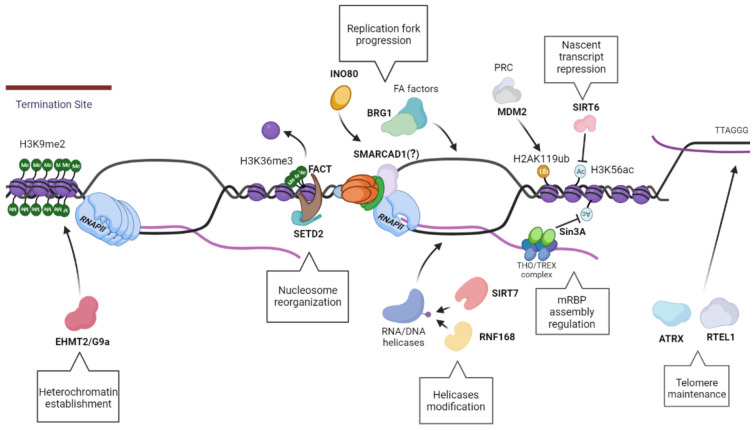
Figure 4.
Schematics showing multiple distinct pathways of R-loop resolution mediated by the Chro-Mates, the chromatin modifying and remodeling factors, described in Section 8 and Section 9. EHMT2/G9a regulates the preservation of the heterochromatin, especially at the termination sites, in order to permit a successful transcription termination. In addition, the nucleosome reorganization upon RNAPII passage is a vital pathway in R-loops resolution, driven by FACT in concert with SETD2. The modification of RNA/DNA helicases has a role in their recruitment and processivity, such as RNF168 ubiquitinates DHX9, while SIRT7 deacetylates DDX21. The homeostasis of the nascent transcript is also essential to regulate R-loop levels, as seen with Sin3A and SIRT6, histone deacetylases that have a role in creating an optimal chromatin status for a proper transcript export and maturation, along with fork progression. Moreover, the integrity of telomeres is preserved via ATRX and RTEL1, which promotes telomere stability and R-loops resolution. Finally, one of the most critical aspects of R-loop resolution is maintenance of fork stability and replication fork progression. This may require factors involved in resolution of R-loops: as seen with MDM2, that promotes fork progression and gene expression; INO80 possibly resolve R-loops by inducing chromatin relaxation; BRG1 works in concert with FA factors to create an open chromatin structure for the recruitment of R-loops resolvases; and Fft3, which can resolve R-loops in fission yeast with its ortholog SMARCAD1 traveling with the replication forks.