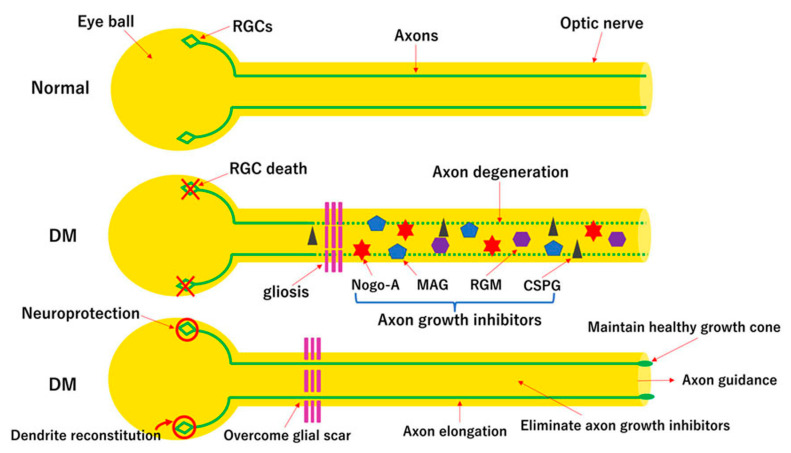
Figure 2.
Scheme of multiple approaches for optic nerve regeneration in diabetic retina. RGCs are vulnerable under diabetic stress (the middle diagram). Therefore, in the early stage, RGCs must be protected. At the same time, however, axons are also degenerated. Thus, degenerated axons must also be regenerated. However, the glial environment of the central nervous system suppresses axonal regeneration because of astrogliosis and myelin debris such as Nogo-A or myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG). For the success of optic nerve regeneration, the RGC death must be blocked and regenerating axons must overcome the glial scar barriers and elongate their axons in the middle of axon growth inhibitors. To overcome these barriers, the growth cone must be maintained in a healthy condition. Finally, regenerating axons must connect to the correct target cells in the brain by regulating axon guidance cues. DM, diabetes mellitus; RGM, repulsive guidance molecule; CSPG, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan.