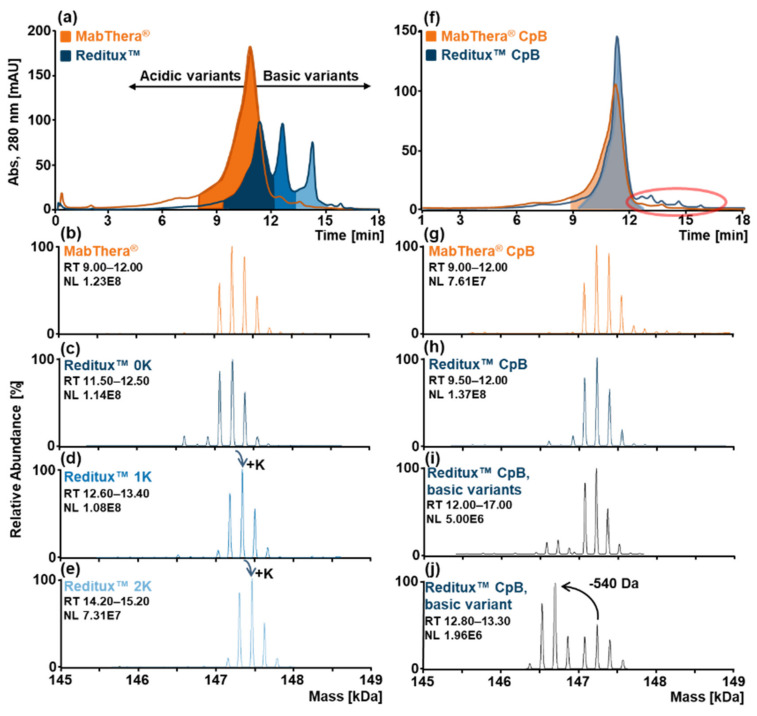
Figure 1.
SCX-HPLC-MS analyses of MabThera® (orange) and Reditux™ (blue). (a) SCX-HPLC-MS chromatogram of intact MabThera® (orange) and Reditux™ (blue). Deconvoluted mass spectrum of (b) MabThera® main variant without C-terminal lysine (0K), (c) Reditux™ variant without C-terminal lysine (0K), (d) Reditux™ variant with one C-terminal lysine (1K), (e) Reditux™ variant with two C-terminal lysine (2K). The three deconvoluted spectra of Reditux™ exhibit the same pattern shifted by +128 Da, corresponding to a lysine residue. (f) SCX-HPLC-MS chromatogram of MabThera® (orange) and Reditux™ (blue) after treatment with carboxypeptidase B (CpB) to remove the C-terminal lysine. The red circle indicates basic variants that are present in Reditux™ and almost completely absent in MabThera®. Deconvoluted mass spectrum of (g) MabThera® main variant with complete clipping of C-terminal lysine (0K), (h) Reditux™ variant with complete clipping of C-terminal lysine (0K), (i) Reditux™ basic variants eluting at RT 12.00–17.00 min, (j) Reditux™ basic variant eluting at RT 12.80–13.30 min. Annotations of the spectra are reported in Tables S2–S6.