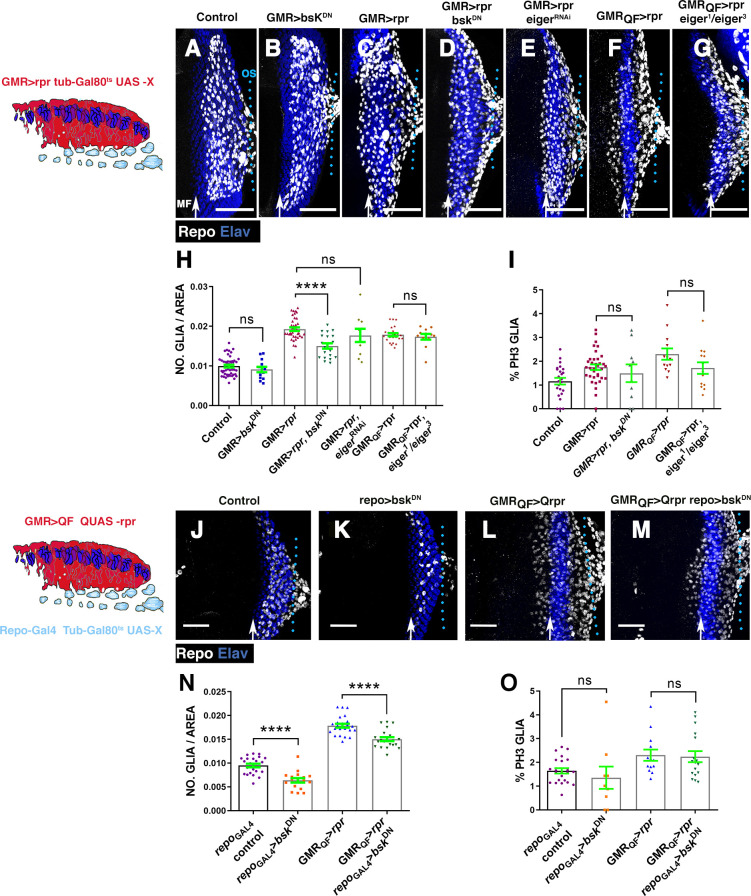
Fig 6. Reduction of JNK activity prevents the accumulation of glial cells produced upon cell death induction.
(A–G and J–M) Projections of confocal images of third instar eye discs stained with anti-Elav (blue) and anti-Repo (white). The schematic illustration on the left represents a transverse section of an eye disc where the region marked in red (expression domain of GMR-Gal4) corresponds to the area of the discs that has been damaged at the same time that JNK was depleted. (A) Control undamaged GMR-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts/+ disc. (B) UAS-bskDN; GMR-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts/+ eye. (C) Damaged UAS-rpr/+; GMR-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts/+ discs. (D) UAS-rpr/UAS-bskDN; GMR-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts/+ damaged discs. (E) UAS-rpr/; GMR-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts/UAS-eigerRNAi. (F) GMR-QF; QUAS-rpr eye discs damaged. (G) Damaged GMR-QF; eiger1/eiger3; QUAS-rpr. All larvae were subjected to the same temperature shifts (see Materials and methods) except larvae of the discs shown in F and G that were raised at 25°C throughout the development. (H–I) Graphs show glial cell density (H) and percentage of mitotic glia cells of discs shown in A–G. (J–M) Effects of the down-regulation of JNK in glial cells of damaging eye discs. In the schematic illustration on the left is indicated in red the region that has been damaged by overexpressing QUAS-rpr under the control of GMR-QF and in light blue glial cells. (J) Control undamaged tub-Gal80ts repo-Gal4 disc. (K) UAS-bskDN /+; tub-Gal80ts; repo-Gal4/+ eye discs. (L) Damaged GMR-QF; tub-Gal80ts; repo-Gal4 QUAS-rpr eye discs. (M) GMR-QF UAS-bskDN; tub-Gal80ts; repo-Gal4 QUAS-rpr damaged discs. (N and O) Graphs show glial cell density (N) and percentage of mitotic glial cells (O) of discs shown in J–M. Scale bars, 50 μm. Statistical analysis is shown in Table F in S1 Text. The numerical data used in this figure are included in S1 Data. GMR, glass multiple reporter; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; RNAi, RNA interference; rpr, reaper.