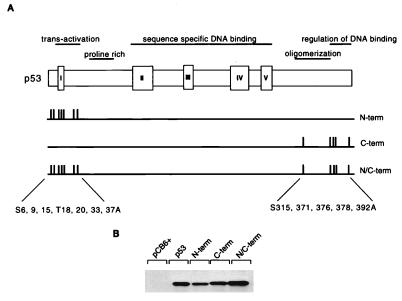
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the human p53 protein indicating the important functional domains (transactivation, proline rich, sequence-specific DNA binding, oligomerization, and regulation of DNA binding), conserved box regions I to V, and potential sites of phosphorylation within the N- and C-terminal regions. To generate N-terminal phosphorylation mutant p53 (N-term), Ser6, Ser9, Ser15, Thr18, Ser20, Ser33, and Ser37 were mutated to Ala in combination. To generate C-terminal phosphorylation mutant p53 (C-term), Ser315, Ser371, Ser376, Ser378, and Ser392 were mutated to Ala in combination. N- and C-terminal phosphorylation mutant p53 (N/C-term) was generated by a combination of the above. (B) Western blot analysis (using PAb1801) of Saos-2 cells transiently expressing wild-type p53 and the p53N-term, p53C-term, and p53N/C-term mutant proteins after transient transfection with 5 μg of the respective plasmid. Cells were harvested at 24 h.