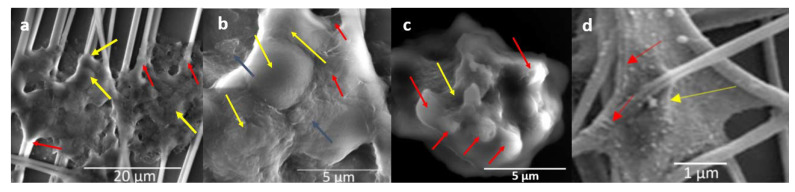
Figure 6.
Environmental scanning electron microscopy of cultured BmVIII-SCC cells adhering to PET nanofibers. (a) Fibrous-like tissue attaching to individual nanofibers (red arrows) suggests the presence of an extracellular matrix (ECM); note the encased cells (yellow arrows) (3000×). (b) Dome-like structures, presumably cells encased in ECM (yellow arrows), flat-sheet morphology of ECM (dark olive arrows), cord-like outer edge of ECM (red arrows) (10,000×). (c) Shallow groove (yellow arrow) suggests prior attachment of an enclosed spheroid (red arrows) to a synthetic nanofiber that was dislodged during fixation (10,000×). (d) Scanning electron micrograph of the mammalian alveolar cell, A645, in 3-D culture with PET nanofiber provided by Nanofiber Solutions, Inc. (Columbus, OH, USA). is shown for comparison exhibiting fibrous nature of the avian-derived extracellular matrix (red arrows), and structural mass encased by the matrix (yellow arrow).