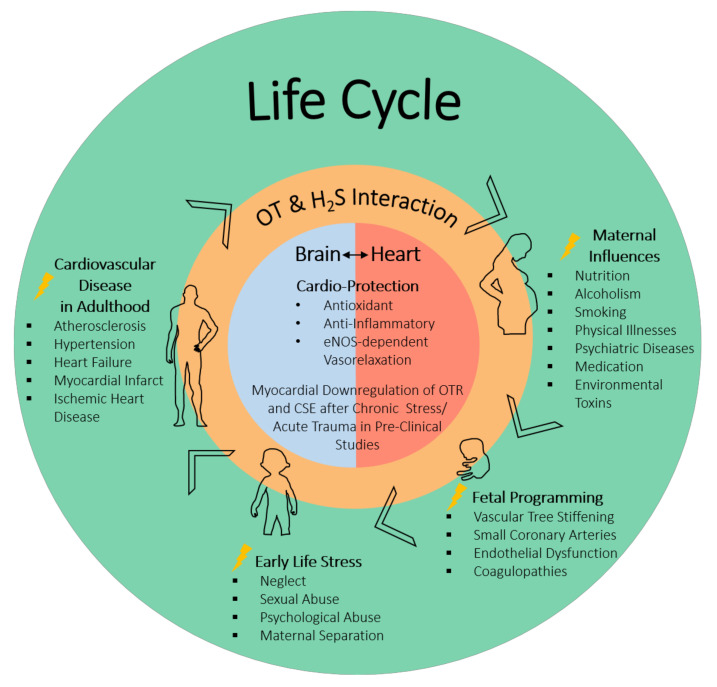
Figure 1.
Interaction of OT and H2S in the brain and the heart: contribution to physical manifestation/protection of ELS-induced CVD in adulthood. ELS affects cardio-vascular programming and the development of CVD in adulthood. Pregnant women who experienced ELS may pass on ELS-triggered behavior/physical conditions: nutrition, smoking, alcoholism, medication/drugs, and illness. Long-term effects on the cardiovascular system of the fetus can be morphological and functional adaptations, stiffening of the vascular tree, small coronary arteries, endothelial dysfunction, reduced number of cardiomyocytes, atherogenic blood lipid profiles, and coagulopathies. Bringing together literature reports on OT and H2S suggests that both are significant common mediators of cardio-protective effects during development as well as in adulthood through their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and eNOS-dependent vasorelaxation. Pre-clinical studies suggest that chronic stress and/or acute trauma leads to a downregulation of the OTR and CSE (the main endogenous H2S-producing enzyme in the vasculature). OT: oxytocin; H2S: hydrogen sulfide; ELS: early life stress; CVD: cardiovascular disease; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; CSE: cystathionine-γ-lyase.