Fig. 4. Polar marine plankton lineages and groups predicted to be most vulnerable to temperature change.
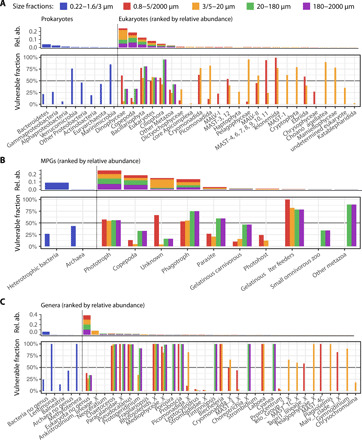
(A) Environmental tolerance range perturbations of the GPI predicted polar marine plankton lineages (community PC1) potentially most affected by temperature variations. (B) Grouping these lineages into MPGs predicted associated functions potentially most affected by temperature variations in the polar ecosystem. (C) Genera most impacted by temperature variations are also identified and are potential species indicators of ocean warming in the polar ecosystem. In all panels, the fraction of lineages, MPGs, and genera (from 1 for most affected to 0 for not affected) predicted to be affected by temperature variations are depicted within each size fraction. Plankton lineages (prokaryotes and eukaryotes), MPGs, and genera are ordered according to the cumulative mean relative abundance of the corresponding OTUs across size fractions (note that these relative abundances are not directly comparable between size fractions).
