Fig. 6.
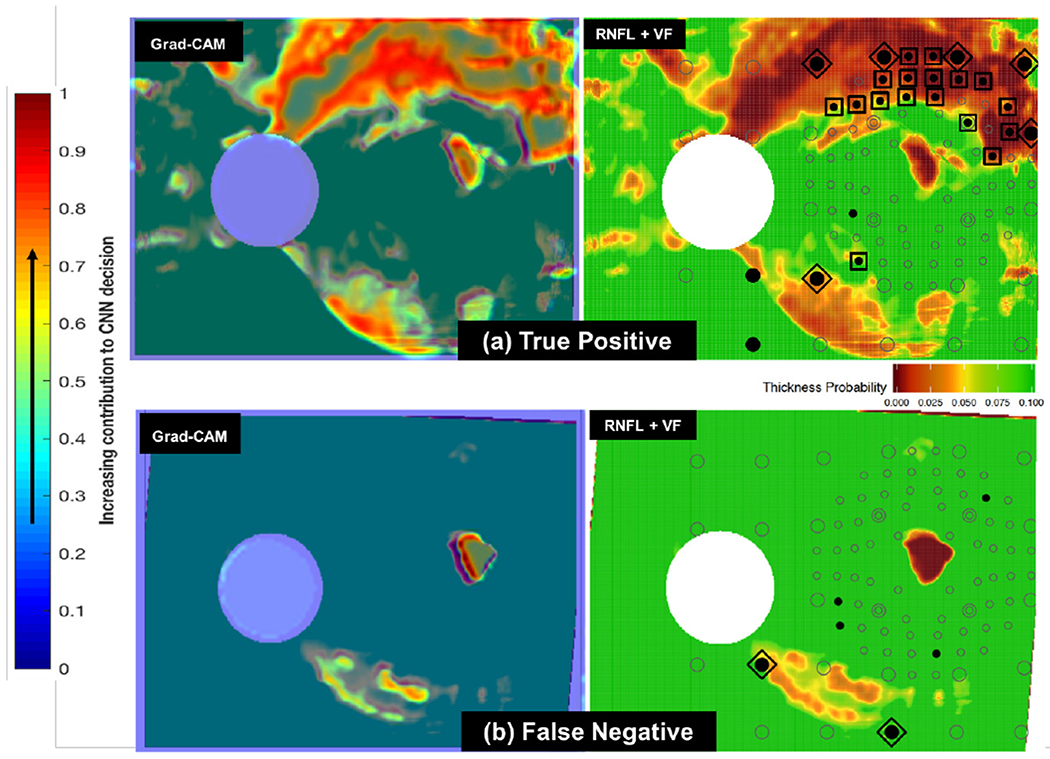
(a): Sample Grad-CAM (at left) for true positive RNFL+VF image (at right). In the RNFL+VF image at right, the open circles are visual field (VF) locations, specific points in the field of view used to test a patient’s functional vision. Filled circles are locations with abnormal visual function; those circumscribed by squares are inner-retina VF locations recognized by clinicians as abnormal both in RNFL and VF (indicative of disease). VF locations circumscribed by diamonds are abnormal outer-retina RNFL+VF locations [14]. Note that there is overlap between highlighted (red and yellow) regions chosen by the CNN as indicative of glaucoma (in Grad-CAM at left) [15] and those locations chosen as abnormal by clinicians (diamonds and squares in RNFL+VF image at right). (b): Sample Grad-CAM (at left) for false negative RNFL+VF image (at right). Note that this false negative (missed case) is challenging, as there are very few highlighted regions chosen both by the CNN as indicative of glaucoma (red/yellow in image at left) and by clinicians as abnormal (diamonds and squares in image at right).
