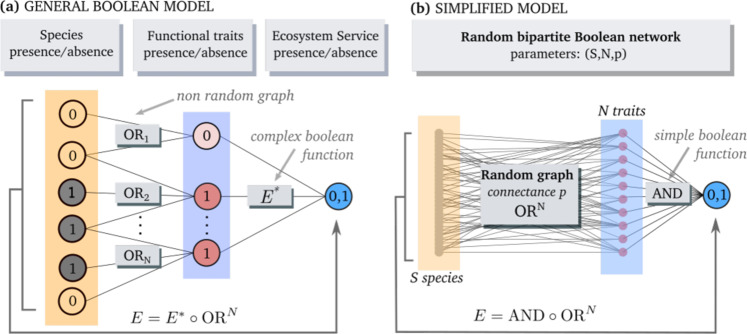
Fig. 2. A Boolean model for ecosystem services.
a We view an ecosystem service as a Boolean function E over the presence/absence configurations of S species (leftmost column). We distinguish species from their N functional traits (middle column). The configuration of any trait n is defined by the logical OR function over the Sn species that share that trait. This amounts to writing E as the composition , which should aim to remove as much functional redundancy as possible from the auxiliary function over trait configurations. b We simplify our model further by (i) considering random species-to-trait associations with connectance p and (ii) choosing the logical AND function for [that is, the least redundant function, which we show (Supplementary Methods) is representative of a random choice across the space of all Boolean functions]. In this model (see ‘Methods’ for full description), we can deduce analytical expressions for the percentiles of the distribution (considering all possible extinction sequences) of robustness of ecosystem service supply R: the fraction of species loss leading to loss of service supply.