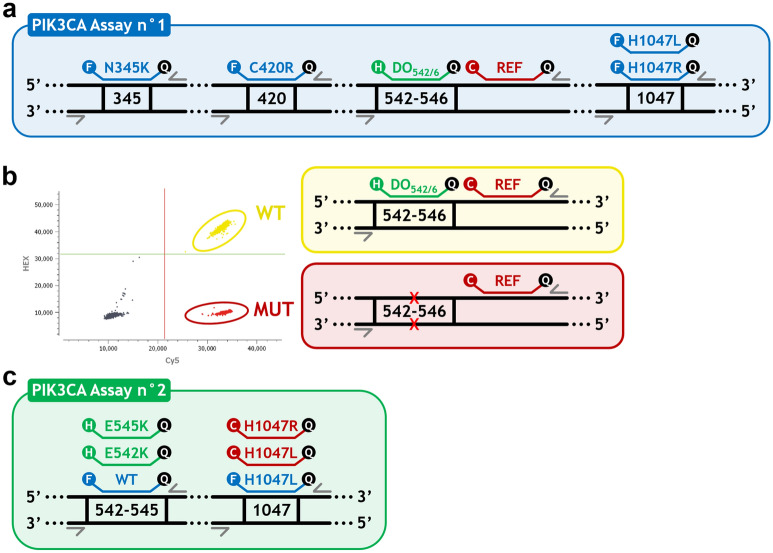
Figure 1.
Design diagrams of the two multiplex assays for PIK3CA mutations detection and Drop-Off542–546 system principle. (a) Design diagram of the PIK3CA Assay n°1: four amplicons are simultaneously amplified using four couples of primers (grey arrows) to permit the detection of N345K, C420R, H1047L and H1047R mutations using FAM-labelled probes (blue color), as well as mutations on codons 542–546 using a HEX-labelled drop-off probe (green color) combined with a Cy5-labelled reference probe (red color). (b) Drop-Off542–546 system principle: WT sequences are detected by both the HEX-labelled drop-off probe and the Cy5-labelled reference probe, thus producing a cluster of HEX-Cy5 double-positive droplets (yellow-colored cluster on the 2D dot plot); whereas sequences bearing mutations (MUT, red crosses) on codons 542 to 546 have sub-optimal or even absent drop-off probe detection (red-colored cluster on the 2D dot plot). (c) Design diagram of the PIK3CA Assay n°2: two amplicons are simultaneously amplified using two couples of primers to permit the detection of wild-type (WT) sequences using a FAM-labelled probe, E542K and E545K mutations using HEX-labelled probes, H1047L mutation using FAM and Cy5-labelled probes and H1047R mutation using a Cy5-labelled probe (C: Cy5; DO: drop-off; F: FAM; H: HEX; MUT: mutation; REF: reference).