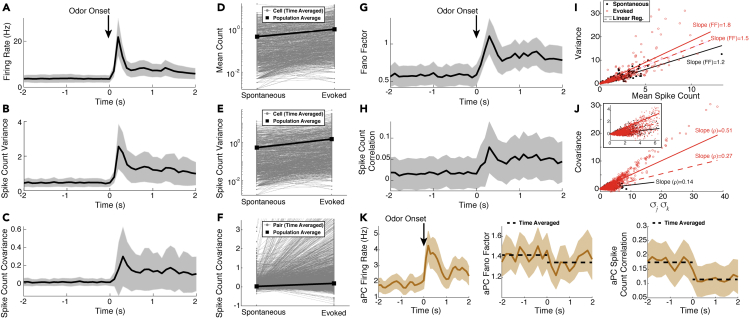
Figure 1.
Spiking statistics from experiments
(A–C) Spiking statistics in spontaneous () and odor-evoked states (); the firing rate (A), spike count variance (B) and covariance (C). (D–F) Trial- and time-averaged spike count statistics of individual cells/pairs in gray (black squares = population average) also generally increase. The mean firing rate (D), 918 out of 1120 cells, 82%), variance (E), 908 out of 1120 cells, 81.1%, vertical log-scale), and covariance (F) 10,194 out of 17,674 cell pairs, 57.7%) increase with odor.
(G–J) Scaled measures of variability shown for completeness. Fano factor (G) and Pearson's Correlation (H) of spike count increase with odor (Ethyl Butyrate).(I) Spike count variance versus mean in spontaneous (black) and evoked (red) states, time-averaged in each state. Lines are regression of best least squares fit to data with 0 intercept, another way to measure Fano factor. Two red lines for evoked state: the solid line (slope of 1.83, ) is regression for all data, lower line (red dashed, slope of 1.52, ) is regression on a subset of data (evoked mean count largest spontaneous mean count) to account for larger mean counts in the evoked state (see mean-matching in Churchland et al., 2010). Spontaneous Fano factor (slope) is 1.21 () is smaller than evoked Fano factor.
(J) Spike count covariance versus product of standard deviations of spike counts. The slope of the regression line is another measure of Pearson's correlation ρ. Spontaneous () and evoked (); evoked with cut-off: ().
(K) Spike statistics from simultaneously recording in the anterior piriform cortex (aPC) are consistent with other data: evoked decreases in Fano factor (Churchland et al., 2010; Miura et al., 2012) and correlation (Miura et al., 2012). Spike counts were binned in 100 ms half-overlapping windows, except for K where 200 ms was used. Data averaged over 10 trials and over cell population (1120 cells in A, B, D, E, G; 17,674 pairs in (C, F, H; 194 cells and 7,395 pairs in K). Shaded gray/tan regions show relative population heterogeneity: std (standard deviation across the population/pairs after trial-averaging; 0.2 scale for visualization).