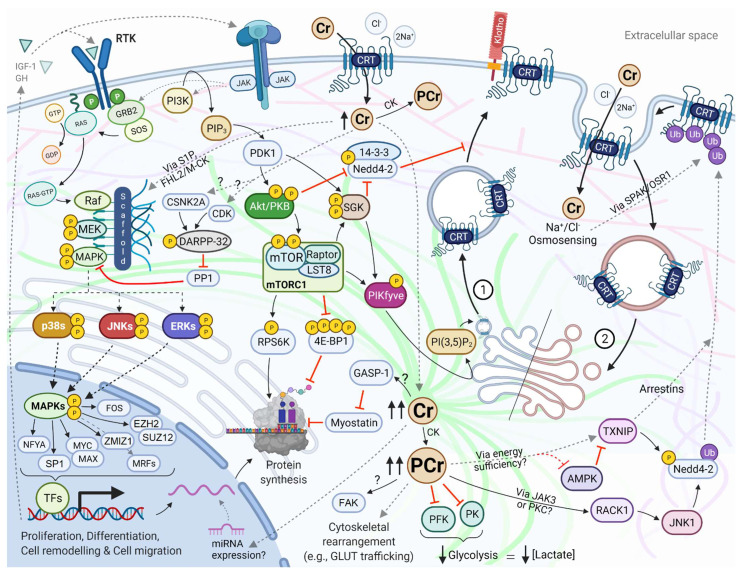
Figure 4.
Bioinformatics- and knowledge-based pathway reconstruction after Cr supplementation. This is a representation of pathways interactions based on the results of our enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes after increasing cellular Cr concentration and the available experimental evidence. This functional network follows the ‘bio-logic’ (integration of bottom-up and top-down directions) of the genotype–outcome interaction. MAPK activation can occur via osmosensing pathways that activate Ras/Raf (e.g., S1P/SPHK1) and mechanosensing pathways that involve mechanical and energy optimization of the cytoskeleton (e.g., Four-and-a-Half Lim 2 is an important mechanosensor that triggers hypertrophy in response to strain and also docks key metabolic enzymes involved in the energy transduction process, such as M-CK, adenylate kinase, and phosphofructokinase). Several subunits of the protein complexes and the architecture of the cytoskeleton are not depicted for readability. We cautiously suggest two dose–response functional pathways for the regulation of the Cr uptake: a kinase-driven mechanism as a result of the initial Cr-enriched environment, which is more related to the anterograde trafficking via endolysosome-specific phosphoinositide compounds (1); and a ubiquitin-driven mechanism that controls the excessive Cr uptake, which is more related to the retrograde trafficking via clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent processes (2). Interlinking protein filaments of the cytoskeleton are represented with lighter-colored lines in the background. See the sections of the manuscript for rationale, citations, and more abbreviations. Dashed arrows represent multiple steps. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CK: creatine kinase; GASP-1: growth and differentiation factor (GDF)-associated serum protein-1; GDP: guanosine diphosphate; GH: growth hormone; GLUT: glucose transporter; GRB2: growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; GTP: guanosine triphosphate; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1; LST8: target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8; MRFs: myogenic regulatory factors; Nedd4-2: E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase NEDD4-like; OSR1: oxidative-stress-responsive kinase 1; PDK1: phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; PFK: phosphofructokinase; PI(3,5)P2: phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate; PIKfyve: 1-phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PK: pyruvate kinase; SGK: serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase; SPAK: SPS1-related proline–alanine-rich kinase; RACK1: receptor for activated C kinase 1; RTK: receptor tyrosine kinases; TFs: transcription factors. Source: created by the authors (D.A.B.) with BioRender—https://biorender.com/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).