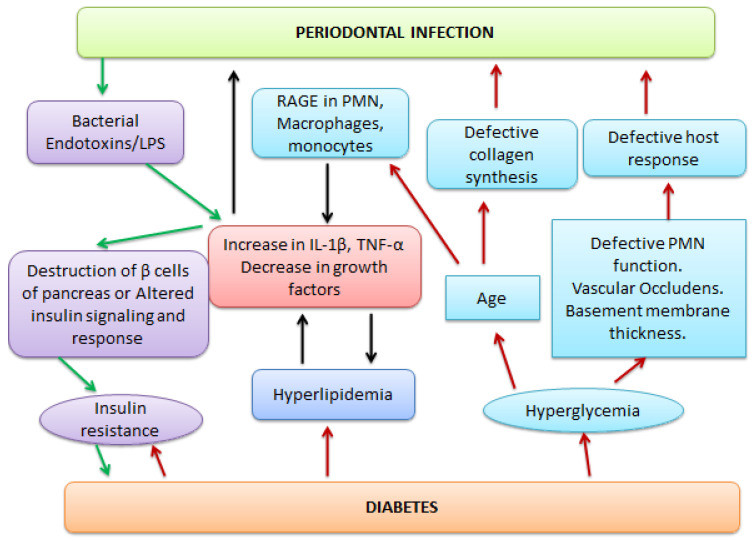
Figure 3.
Two-way link of periodontitis with diabetes. Bacterial endotoxins lead to an increase in interleukin (IL-1β) and the tissue necrosis factor (TNF-α) which results in hyperlipidemia. This also leads to the destruction of β cells of the pancreas and hence insulin resistance. In the reverse direction, the hyperglycemia leads to defective polymorphonuclear neutrophils’ (PMN) functions, defective host response, and collagen synthesis, which promotes RAGE (receptors of advanced glycation end-products) in PMN. All these factors ultimately aggravate the periodontal infection.