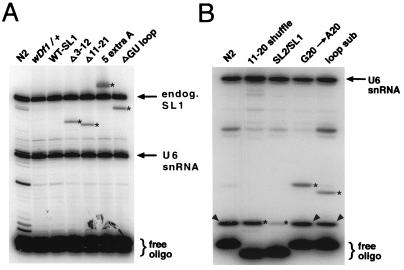
FIG. 4.
Primer extension analysis of mutant SL RNA expression. (A) Analysis of mutant SL RNAs which differ in size from the endogenous (endog.) SL1 RNA. RNA was prepared from mixed-stage animals carrying the indicated mutant SL RNA transgene. A labeled primer that recognizes a portion of the SL1 RNA intron was used (see Materials and Methods). Since the populations contained heterozygous mutant and wild-type animals, primer extension yields both an endogenous SL1 RNA product (upper arrow) and the mutant leader SL RNA product (stars). RNA analysis of wild-type animals (N2) and heterozygous deletion mutant animals (wDf1/+) are shown as controls, demonstrating that the products detected in the mutant strains are specific for those strains. All constructs shown were analyzed in a wDf1/+ genetic background. No additional products were detected in the WT-SL1 sample (SL1 RNA transcribed from the U2-3 promoter), indicating that this RNA is apparently of wild-type length. A labeled primer specific for a portion of the U6 snRNA (lower arrow) was included in the reaction; its extended product serves as a control for loading of comparable amounts of RNA in each lane. (B) Analysis of mutant SL RNAs which are the same size as the endogenous SL1 RNA. RNA was prepared from mixed-stage wild-type or wDf1/+ animals carrying the indicated mutant SL RNA transgene (as in panel A). In order to distinguish mutant from endogenous wild-type SL1 RNA, a dideoxy primer extension reaction was performed. The RNA was extended with a labeled primer specific for a portion of the SL1 RNA intron-like sequence or leader sequence (see Materials and Methods). Dideoxycytosine was included in the reaction mixture to interrupt extension of the SL RNAs; because of the differences in sequence between mutant leaders (stars) and wild-type endogenous SL1 RNA (arrowheads), products are extended to different lengths for each RNA. In the case of the 11–20 shuffle and SL2-SL1 chimeric RNAs, labeled primers were used that recognized these RNAs specifically; thus, the endogenous RNA is not extended and the band migrating at the same position as wild-type SL1 is exclusively the mutant RNA. A U6 RNA primer (arrow) was used to control for loading, as in panel A.