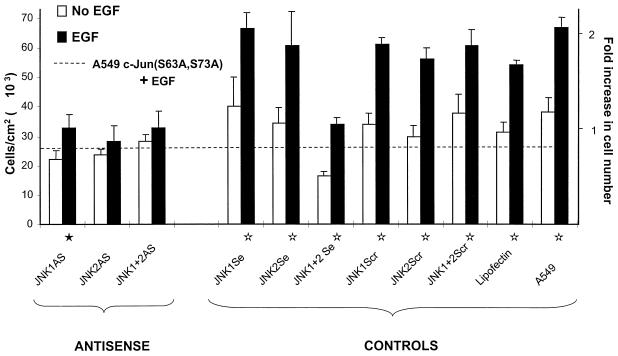
FIG. 7.
JNK2AS preferentially inhibits EGF-induced proliferation in A549. Proliferation assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods with the unmodified oligonucleotides. The cells were maintained in 0.5% FBS during the experiment. Five days after the treatment with 0.1 μM rhEGF, the cells were counted with a Coulter counter. The dashed line indicates the growth attained by A549 cells that stably express the dominant-negative inhibitor c-Jun(S63A,S73A) which is known to be inhibited from responding to rhEGF (7). The proliferation data shown here are the average of two identical and independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate. Fold increase in cell number is given considering 1 as the average number of cells grown in the absence of rhEGF. The standard errors (error bars) are given as √(ς12 + ς22), where ς1 and ς2 are the standard errors of the replicate experiments. Statistical analyses were carried out with the combined data of both replicates by analysis of variance implemented with Systat software. The statistical significance for EGF-induced growth was P < 0.002 (⋆) or P < 0.05 (★).