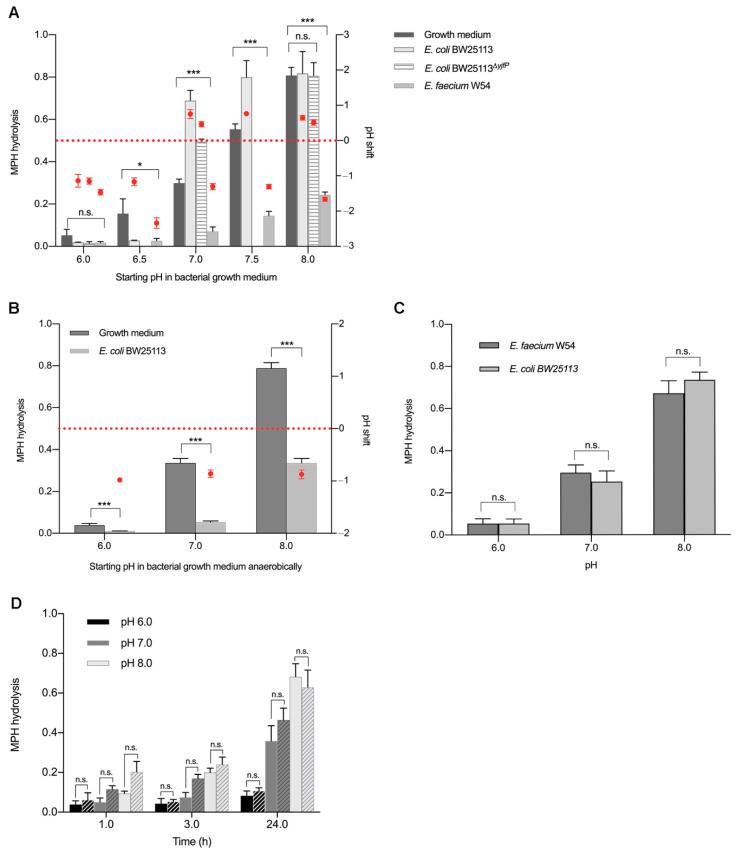
Figure 3.
Effect of pH on methylphenidate hydrolysis in the presence and absence of bacterial esterases. Methylphenidate hydrolysis at different starting pH in (A) bacterial growth medium, E. coli BW25113, E. coli BW25113ΔyjfP and E. faecium W54 pure cultures, (B) E. coli BW25113 pure cultures anaerobically, (C) E. coli BW25113 and E. faecium W54 bacterial supernatants and (D) E. coli BW25113 cell lysates (solid bars) and phosphate buffer control (striped bars). Methylphenidate hydrolysis quantified in ng/µL and normalized to d10-ritalinic acid (left y-axis; grey bars) and pH changes during bacterial growth are shown as pH shift after 24 h (red dots; right y-axis). Error bars represent SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.