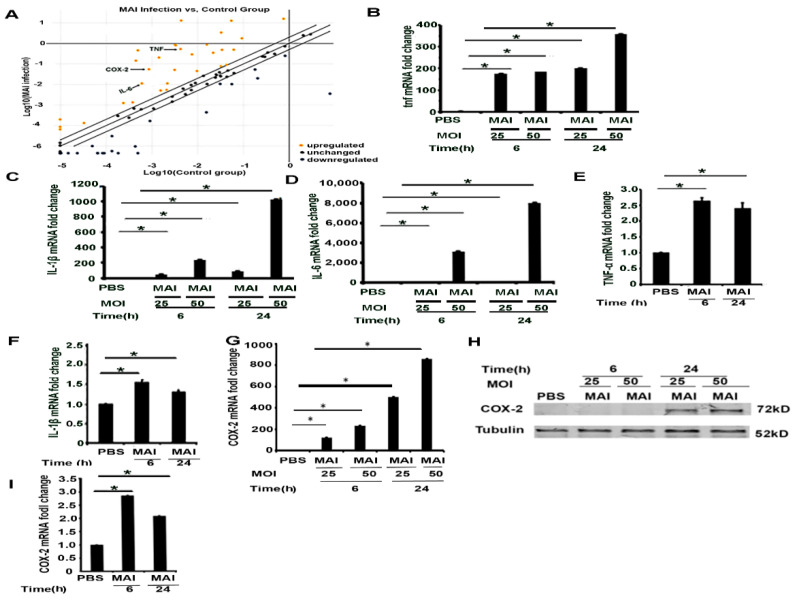
Figure 2.
Infection of murine and human macrophages with MAI activates inflammatory cytokines and the COX-2 signaling pathway. Mouse BMDM were infected with MAI (MOI: 25) for 6 h. (A) Cells were lysed to assess the profiling of mRNA using the inflammatory responses and autoimunity-RT2 profile PCR array. Yellow dots indicate increased mRNA, and blue dots indicate decreased miRNAs (more than twofold). Data are form n = 2 biological replicates. COX-2 is labelled by a black arrow. BMDM were infected with MAI (MOI: 25 or MOI: 50) for 6 h and 24 h. mRNA levels of TNF, IL-1B, and IL-6 were determined by quantitative PCR, as shown in (B–D). Human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) were infected with MAI for 6 h and 24 h. Expression levels of TNF and IL-1β in MDM were detected, (E,F). BMDM were infected with MAI (MOI: 25 or MOI: 50) for 6 h and 24 h. mRNA and protein levels of COX-2 was determined by quantitative PCR and Western blot, as shown in (G,H). MDM were infected with MAI (MO1: 25) for 6 and 24 h. The mRNA level of COX-2 was quantified by quantitative RT-qPCR in MDM treated with or without MAI, as shown in (I). The one-way ANOVA test was used, and all data are presented as mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05.