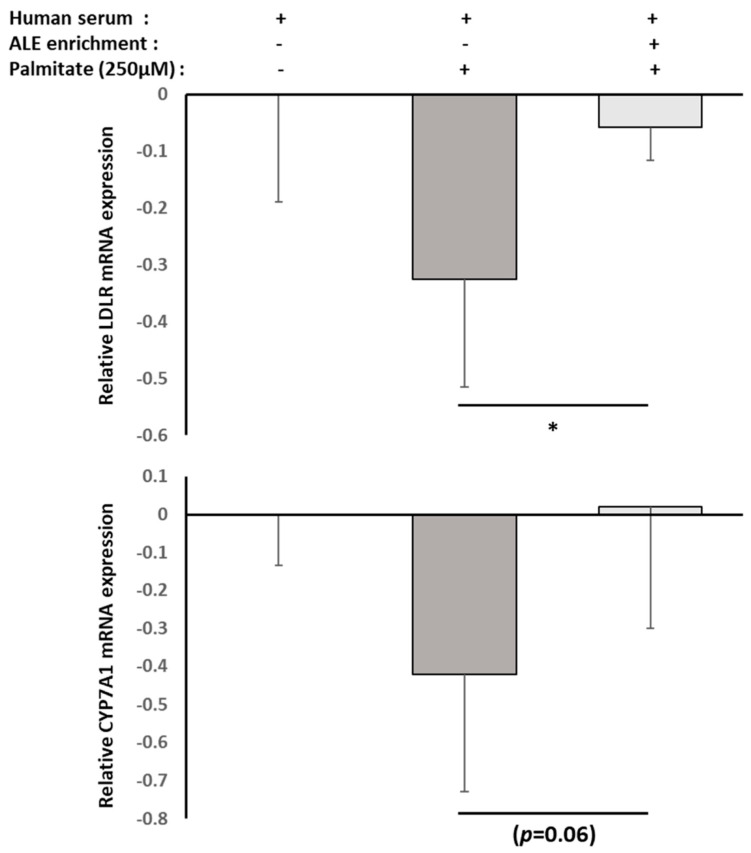
Figure 7.
Effect of human serum enriched with ALE metabolites on LDLR and CYP7A1 mRNA expression levels in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were preincubated with human serum enriched with ALE metabolites for 24 h and stimulated with palmitate (250 µM) for an additional 48 h (− absence; + presence). LDLR and CYP7A1 mRNA expression levels in HepG2 cells were measured by RT-PCR (PowerUp SYBRgreen, Applied Biosystems). β-Actine was used as a housekeeping gene. Primers were designed as follows: LDLR-F: AAA GTT GAT GCT GTT GAT GTT CT; LDLR-R: TGG CAG AGG AAA TGA GAA GAA G; CYP7A1-F: GCT TTC ATT GCT TCT GGG TTC; CYP7A1-R: GAT GAT CTG GAG AAG GCC AAG; ACTB-F: ATT GGC AAT GAG CGG TTC; and ACTB-R: GGA TGC CAC AGG ACT CCA. Palmitate-induced inhibition of both LDLR and CYP7A1 mRNA expressions was reduced by the presence of ALE metabolites. Significance was reached for LDLR with * (p < 0.05). p-value for CYP7A1 is p = 0.06.