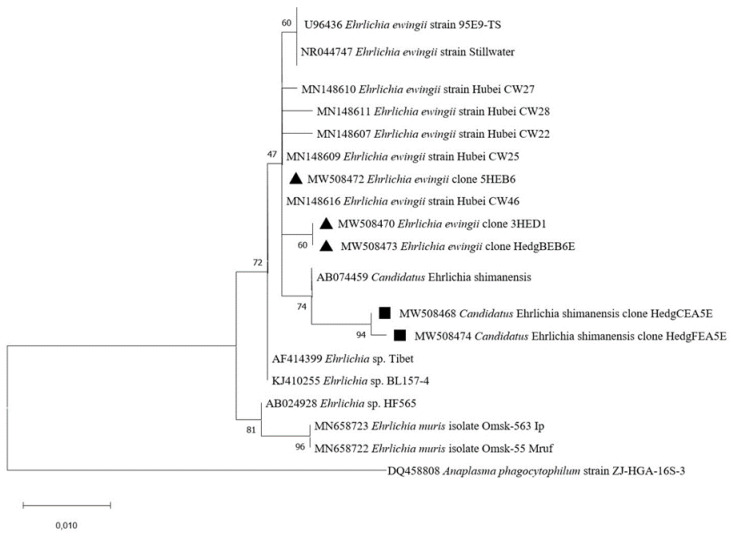
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA sequences of Ehrlichia spp. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA sequences of Ehrlichia spp. using the maximum likelihood method based on the General Time Reversible model. In the phylogenetic tree, GenBank sequences, species designations and strain names are given. The sequences investigated in the present study are marked with a black triangle (E. ewingii) and black square (Ca. E. shimenensis). The tree with the highest log likelihood (−952.31) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches (bootstrap values). A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (5 categories (+G, parameter = 200.0000)). The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable ([+I], 37.52% sites). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. This analysis involved 22 nucleotide sequences. There were a total of 510 positions in the final dataset.