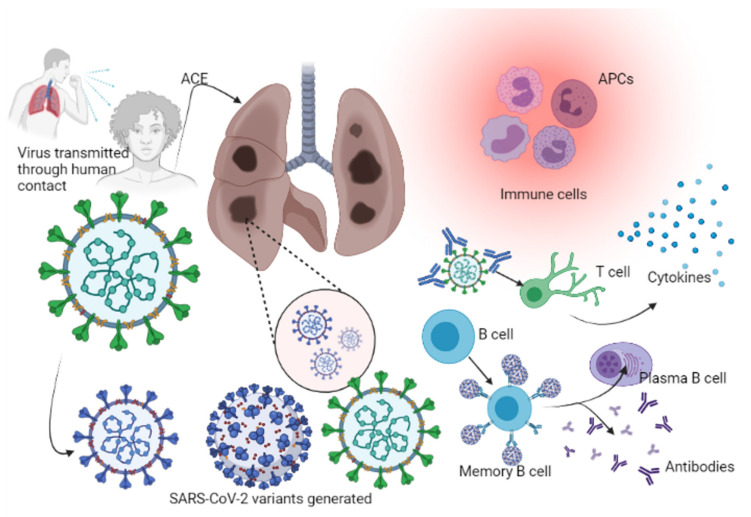
Figure 2.
Immunopathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in humans. Colonization by SARS-CoV-2 is enhanced by ACE through which further viral replication takes place. Increased viral exposure leads to the generation of variants. Immune cells (APCs) including basophils, neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes help to identify the infection. APCs work with T cells by binding to specific T cell receptors, which leads to the activation of CD4 and CD8 cells and the production of cytokines. The humoral response involves B cells, which are activated once an APC cell presents the antigen through the B cell receptors, leading to the activation of memory B cells and plasma B cells for the production of more antibodies to neutralize infection.