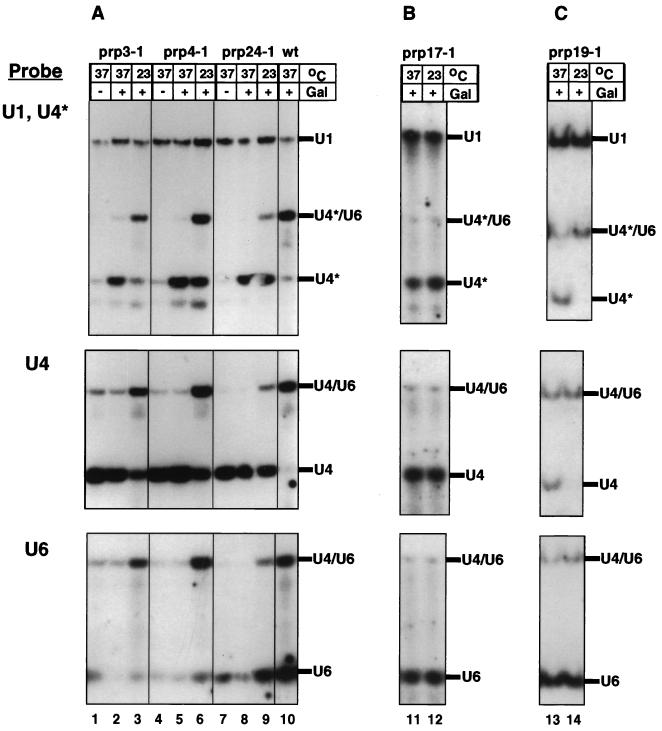
FIG. 2.
U4/U6 assembly defects of splicing-defective mutants. The prp3-1, prp4-1, and prp24-1 strains and a wild-type (wt) strain (A), the prp17-1 strain (B), and the prp19-1 strain (C), all transformed with the galactose-inducible U4* gene, were grown for 30 min at 37°C (lanes 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, and 13) or left at 23°C (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 14). Production of U4* was subsequently induced by addition of galactose (Gal) (except in lanes 1, 4, and 7), and growth was continued at the same temperature for another 2 h. Total cell RNA was extracted, separated on a native polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a nylon membrane, and hybridized with radioactively labelled oligonucleotides complementary to U4* and U1 (loading control) snRNAs (upper panels). The same filters (after removal of the U1 and U4* probes) were hybridized with an oligonucleotide probe specific to the wild-type U4 snRNA (middle panels) and subsequently with a U6-specific probe (lower panels).