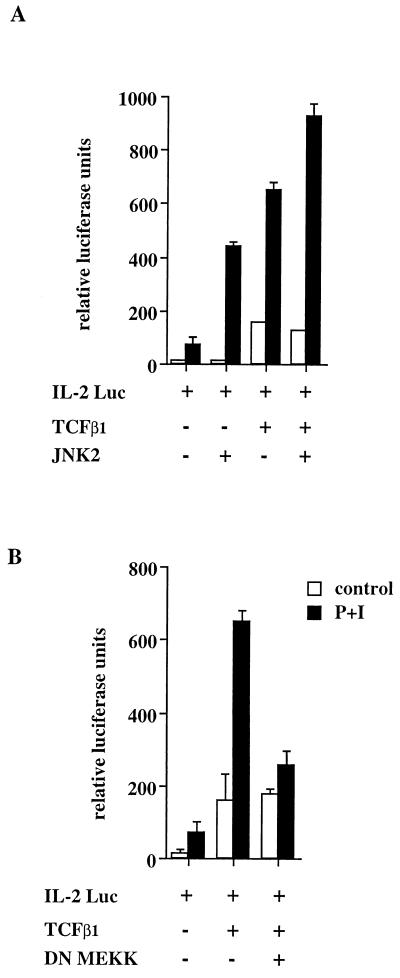
FIG. 10.
The ability of TCFβ1 to induce activation-dependent transactivation of the IL-2 promoter is JNK dependent. (A) TCFβ1 enhances the activation-inducible transcription of the IL-2 promoter. Jurkat T cells were transfected with a minimal promoter from the IL-2 gene cloned into a luciferase reporter plasmid (9). The activation-dependent transcription from the IL-2 promoter was enhanced by cotransfection with a TCFβ1 expression plasmid or a JNK2 expression plasmid. Cotransfection of both TCFβ1 and JNK2 expression plasmids further enhanced transcription from the cotransfected IL-2 reporter plasmid. Cells were activated with PMA plus ionomycin for 12 to 18 h, harvested, and assayed for luciferase activity as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The dominant-negative mutant of MEKK (K432M) inhibits the ability of TCFβ1 to enhance inducible transcription from the IL-2 promoter. Jurkat T cells were transfected with the IL-2 reporter plasmid and either left unactivated or activated with PMA plus ionomycin (P+I) for 12 to 18 h. Cells were cotransfected with TCFβ1 alone or with the catalytically inactive MEKK (K432M) expression plasmid. The dominant-negative mutant of MEKK inhibits inducible, but not basal, transactivation by TCFβ1.