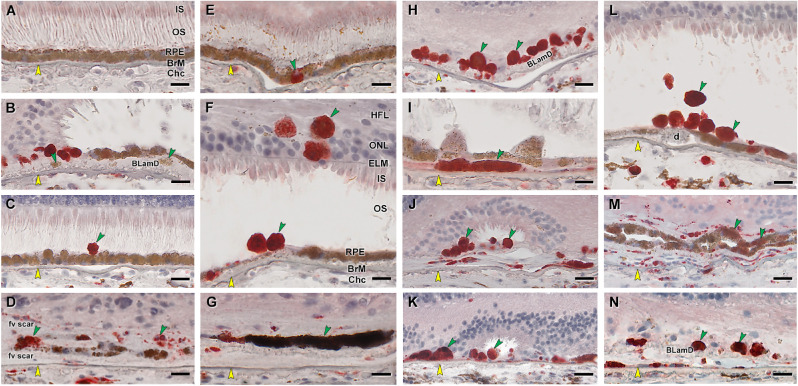
Figure 5.
RPE corresponding to HRF and other abnormal cells are CD68+. Twenty donor eyes (16 AMD, 4 controls; eye numbers in Supplementary Table S7) were used for immunohistochemistry with mouse monoclonal anti-human CD68 (Supplementary Table S1) and red reaction product. Fourteen of 16 previously described morphologic phenotypes of RPE27 were identified (Supplementary Table S2). All scale bars are 20 µm; yellow arrowheads indicate BrM, and green arrowheads indicate abnormal RPE phenotypes. (A) CD68– “uniform” RPE, unremarkable (#1). (B) CD68– granule aggregates, released basally from “shedding” RPE; atrophic AMD (#13). (C) CD68+ “sloughed” RPE; atrophic AMD (#12). (D) Both CD68+ and CD68– “entombed” RPE; neovascular AMD (nvAMD) (#18). (E) A single CD68+ “nonuniform” RPE from a less-affected area, nvAMD (#20). (F) CD68+ “intraretinal” RPE; early to intermediate AMD (#7). (G) Variable CD68 immunoreactivity in “melanotic” RPE, nvAMD (#18). CD68 immunoreactivity is variable on heavily and light pigmented melanotic RPE. (H) CD68+ “severe” RPE; atrophic AMD (#13). (I) CD68+ “subducted” RPE, atrophic AMD (#12). (J) CD68+ “entubulated” RPE, atrophic AMD (#12). (K) CD68+ “dissociated” RPE, atrophic AMD (#12). (L) CD68+ “dissociated” RPE and “sloughed” RPE, early to intermediate AMD (#7). (M) Variable CD68 immunoreactivity in “bilaminar” RPE, nvAMD (#20). (N) CD68+ “dissociated” RPE; atrophic AMD (#12). ChC, choriocapillaris; d, drusen; fv scar, fibrovascular scar; IS, inner segments of photoreceptors; OS, outer segments of photoreceptors.