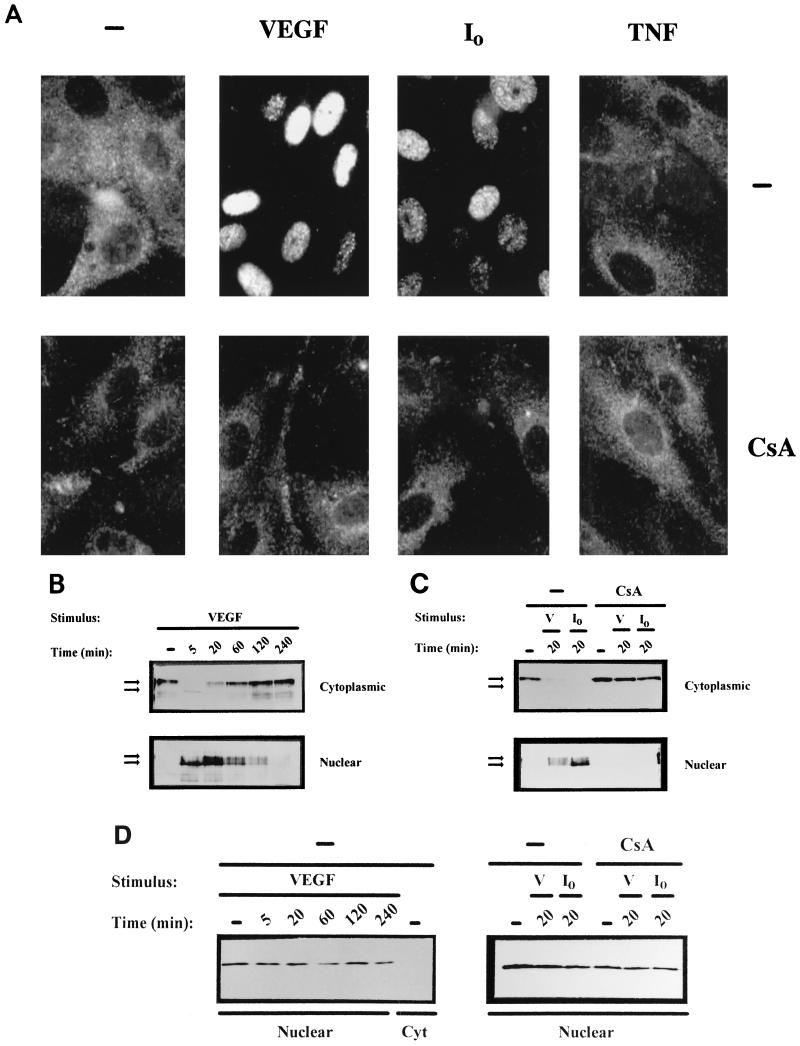
FIG. 1.
VEGF induces dephosphorylation and nuclear localization of NFATp in HUVECs. (A) Immunocytochemical staining of HUVECs unstimulated (−) or treated with VEGF (50 ng/ml), the calcium ionophore A23187 (1 μM) (I0), or 25 ng of TNF-α per ml for 20 min. The cells were either untreated (top panels) or incubated with 200 ng of CsA per ml (bottom panels) for 2 h prior to the addition of the stimuli. After stimulation, the cells were fixed and stained with the anti-NFATp antiserum 67.1. (B and C) HUVECs, either pretreated or not (−) with CsA (200 ng/ml) for 2 h, were left untreated (−) or stimulated with VEGF (50 ng/ml) or calcium ionophore (I0) (1 μM) for the indicated times. Fractionated cytoplasmic or nuclear extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with the 67.1 antiserum for NFATp detection. The mobilities of the upper and lower bands, corresponding to phosphorylated and dephosphorylated forms of NFATp, respectively, are indicated by arrows. (D) As a control for the fractionation process, aliquots of the extracts used for NFATp detection were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of nuclear PCNA. Cyt, cytoplasmic; V, VEGF.