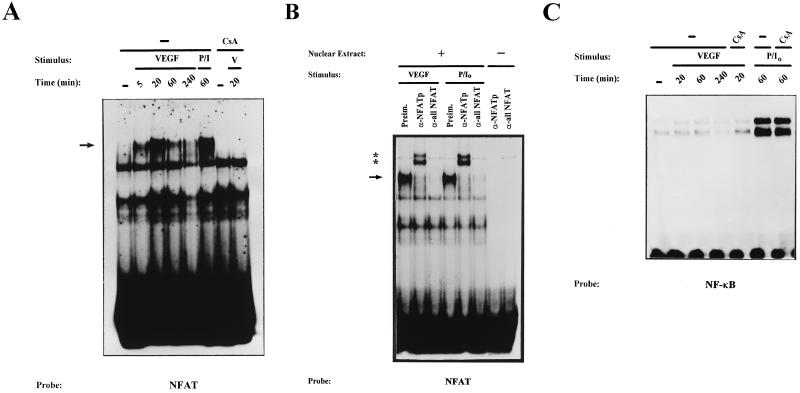
FIG. 2.
Kinetic analysis and serological characterization of the NFAT DNA-binding complexes induced by VEGF. Nuclear extracts from HUVECs stimulated for the indicated times with VEGF (50 ng/ml) (V) or a combination of PMA (20 ng/ml) plus ionophore (1 μM) (P/I0) or pretreated with CsA (200 ng/ml) for 2 h before stimulation were analyzed by EMSA. (A) Analysis of the DNA-binding activity to the NFAT probe of the IL-4 promoter in nuclear extracts from HUVECs activated for different times with VEGF (VEGF or V). EMSAs with extracts from VEGF-activated cells pretreated with CsA as well as control extracts from PMA- plus ionophore-treated cells are shown. The mobility of the specific VEGF-induced (CsA-sensitive) complex is indicated by an arrow. (B) Serological characterization of the NFAT DNA-binding complexes. EMSAs were performed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of nuclear extracts from cells activated with VEGF or PMA plus ionophore that were incubated with 0.5 μl of either preimmune serum (Preim.), anti-NFATp antiserum 67.1, or the anti-NFAT family antiserum 796 for 15 min prior to the addition of the labeled probe. The VEGF-induced NFAT complex and the supershifted complexes induced by the anti-NFATp 67.1 are indicated by an arrow and asterisks, respectively. (C) Nuclear extracts from HUVECs treated as in panel A were analyzed for NF-κB binding with the κB site of the IL-2 promoter as a probe.