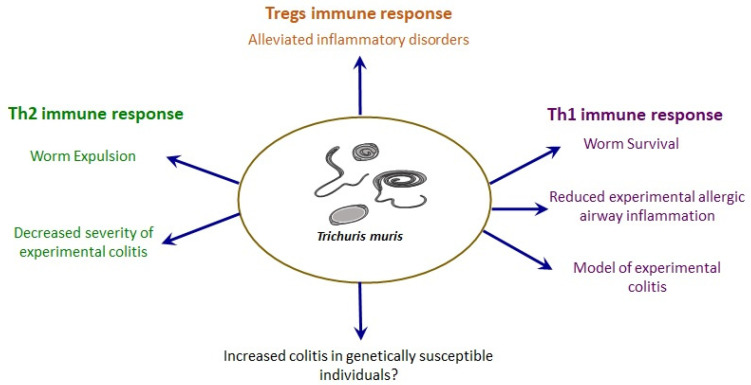
Figure 2.
Overview of the role of T. muris in inflammatory and immunogenic diseases. T. muris modulates immunopathological and inflammatory disorders by triggering Th1/Th2/Tregs immune responses [9]. Acute T. muris infection results in mounting Th2 immune responses, which are associated with worm expulsion and reduced severity of chemical-induced colitis [135]. However, the effect of T. muris infection in colitis in genetically susceptible individuals remains to be determined. Chronic T. muris infection leads to Th1 immune responses resulting in worm survival and protection against allergic airway diseases [146]. Chronic T. muris infection model can also be used as a model of experimental colitis [144]. T. muris infection also induces regulatory Tregs, and consequently these cells, by releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines, reduce inflammatory disorders [141].