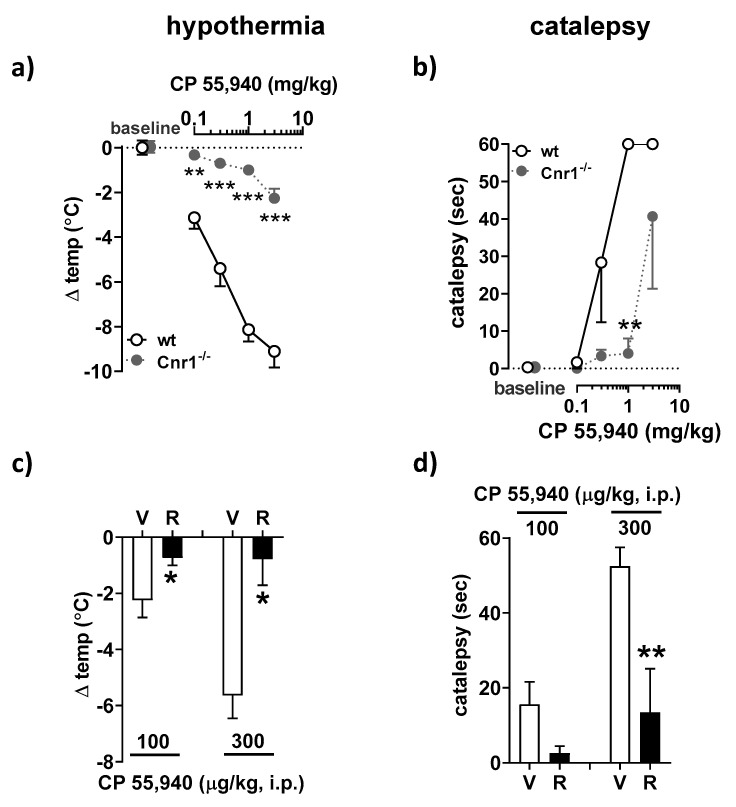
Figure 1.
Effect of central administration of rimonabant on CP 55,940-induced catalepsy and hypothermia in mice. (a,b) Pharmacologically naïve Cnr1−/− (ko) mice and wild-type littermates (wt) were injected with CP 55,940 (0.1, 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg; i.p.) at 30 min intervals. Body temperature (a) and cataleptic behavior (b) were evaluated before administering the next dose of CP 55,940. The respective baseline body temperature in wt and ko groups prior to CP 55,940 injection were 37.1 ± 0.3 °C (n = 3) and 37.2 ± 0.3 °C (n = 3). Mice held the bar for 0.3 ± 0.3 s and 0.3 ± 0.3 s in wt and ko groups, respectively. (c,d) Conscious freely moving C57BL/6J mice (n = 5 animals per treatment group) were infused intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) with rimonabant (2 µg, R) or its solvent (V), followed 30 min later by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of CP 55,940 (0.1 or 0.3 mg/kg). Another 30 min passed before the hypothermic (c) and cataleptic (d) responses were measured. The respective baseline body temperatures before CP 55,940 injection to V- and R-infused groups were 37.6 ± 0.1 °C and 37.5 ± 0.1 °C (n = 10). Mice held the bar for 0.3 ± 0.3 s and 0.1 ± 0.1 s in V- and R-treated groups, respectively. Results are means ± s.e.m. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.01 compared to Cnr1−/− mice (a,b); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared to vehicle (c,d).