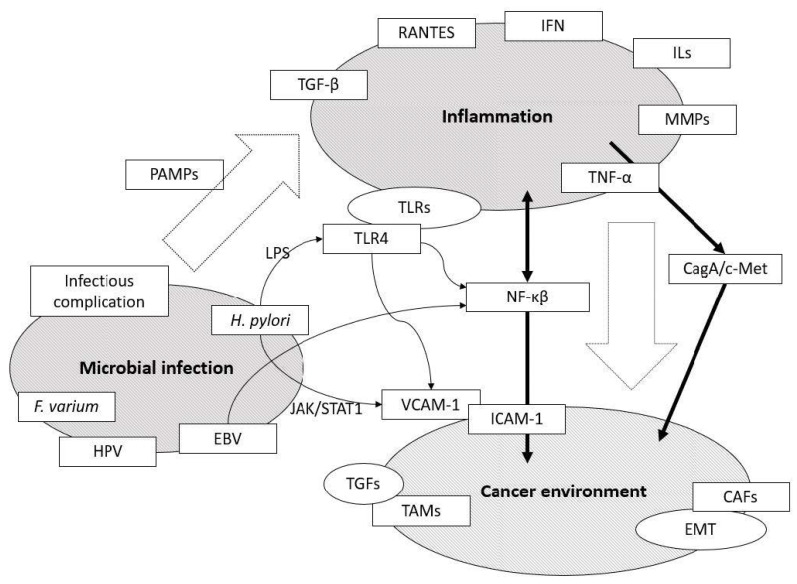
Figure 1.
An overview of the links between microbial infection, chronic inflammation, and cancer environment. Several signaling pathways, such as TLR4 and CagA/c-Met, and mediators selected by microbial inflammation play an important role in the development of gastrointestinal cancers. EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; CAFs: Cancer associated fibroblasts; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; HPV: Human papilloma virus; IFN: Interferon; ILs: Interleukins; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; JAK/STAT1: Janus kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide, MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; NF-κβ: nuclear factor-kappa β; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules; RANTES: Regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; TAMs: Tumor associated macrophages; TGFs: Transforming growth factor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.