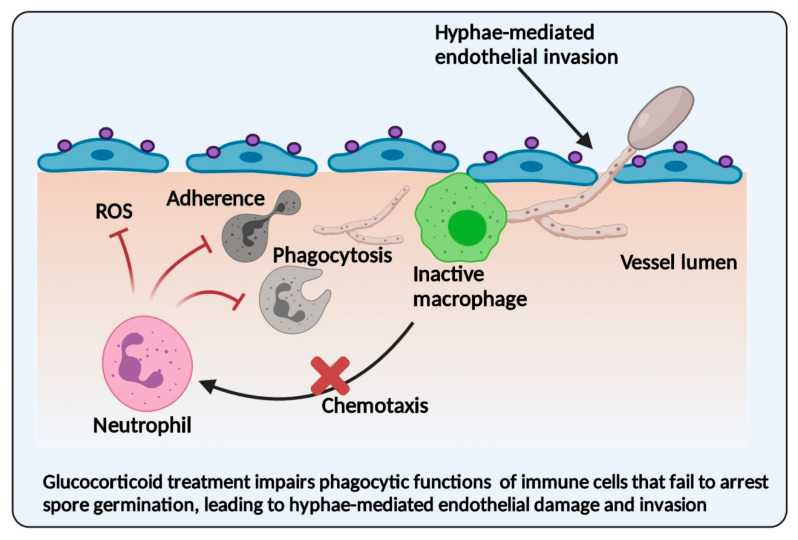
Figure 3.
Corticosteroid therapy-induced immune dysfunction in COVID-19-associated mucormycosis. Corticosteroid therapy and diabetes mellitus attenuate the phagocytic functions of immune cells that allow the germination of Mucorales spores, leading to angio-invasion and tissue necrosis. Corticosteroid treatment impairs adherence, chemotaxis, phagocytosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, failing to arrest spore germination and leading to hyphae-mediated endothelial invasion and damage.