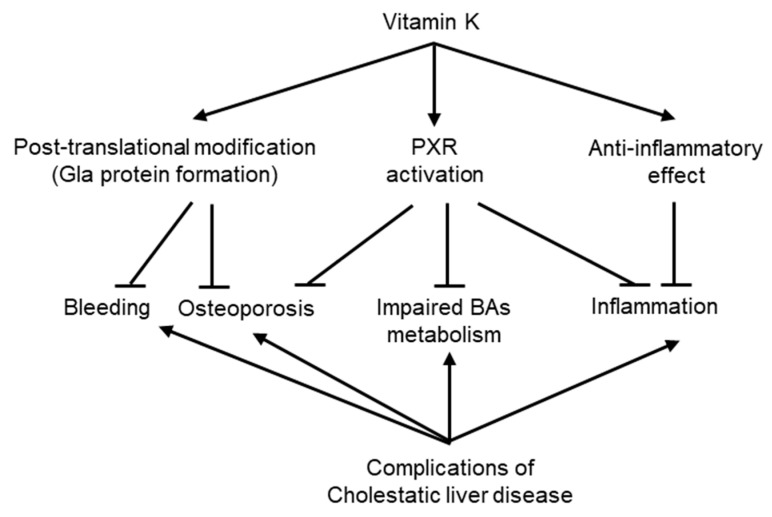
Figure 3.
Potential roles of vitamin K in cholestatic liver disease. VK plays several important roles to ameliorate the complications of cholestatic liver disease, at least through three modes of action—posttranslational modification, which allows the formation of several important Gla proteins, leading to the suppression of bleeding and osteoporosis; PXR activation, which may reduce osteoporosis and inflammation, as well as correct BA metabolism; and an anti-inflammatory effect.