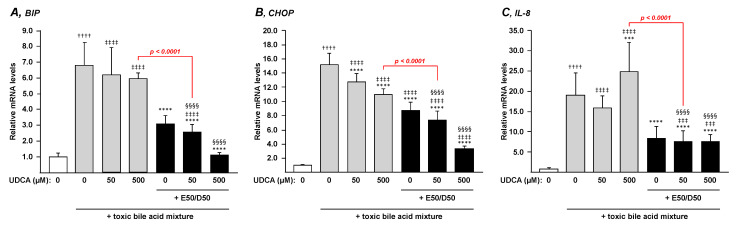
Figure 3.
N-3 PUFAs strongly improve the ability of low and high UDCA doses to prevent ER stress and inflammation. HepG2 cells were exposed to vehicle (DMSO) or a toxic BA mixture (i.e., CA, CDCA, LCA and DCA, 100 µM each) for 24 h in the absence or presence, of EPA/DHA (50/50 µM), UDCA (50–500 µM), or the EPA/DHA + UDCA combinations. Total RNA was extracted and analyzed for transcript levels of the ER-stress BIP (A) and CHOP (B) and inflammatory IL-8 (C) markers by qRT-PCR as detailed in the materials and methods section, and mRNA levels were expressed relatively to control cells set at 1. Data represent the mean of two independent experiments in which each treatment was performed in quadruplicate. Each data point therefore corresponds to the mean of 8 replicates ± SD. Statistical significances as determined by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc were as follows: Untreated cells exposed to vehicle vs. untreated cells exposed to BA: †††† p < 0.0001; Vehicle cells vs. UDCA treated cells: ‡‡‡ p < 0.001; ‡‡‡‡ p < 0.0001; BA exposed cells vs. BA + UDCA ± EPA/DHA exposed cells: *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001; UDCA treated cells vs. UDCA + EPA/DHA treated cells: §§§§ p < 0.0001.