Table 1.
Screening data of the N-formylation of amine 1.
| Entry | Catalyst | Base | TON 2 | Yield 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe3O4 | NaOH | 0 | N. D. 4 |
| 2 5 | Pd–Fe3O4 | NaOH | 20 | 55 |
| 3 6 | Au–Fe3O4 | NaOH | 9 | 25 |
| 4 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | NaOH | 23 | 65 |
| 5 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | - | 5 | 14 |
| 6 7 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | NaOH | 15 | 43 |
| 7 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | Cs2CO3 | 25 | 69 |
| 8 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | CsOH·H2O | 33 | 90 8 |
| 9 9 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | CsOH·H2O | 33 | 92 (84 10) |
| 10 11 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | CsOH·H2O | 32 | 89 |
| 11 12 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | CsOH·H2O | 15 | 42 13 |
| 12 14 | AuPd–Fe3O4 | CsOH·H2O | 89 | 71 |
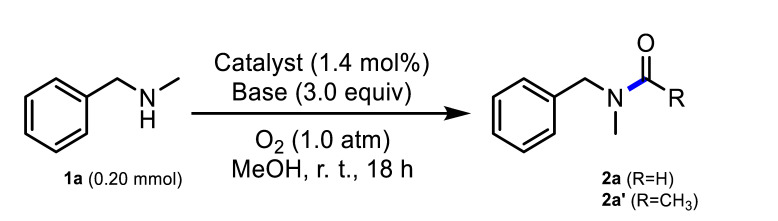
1 Reaction conditions: 1a (0.20 mmol), catalyst (1.4 mol%), base (3.0 equiv), O2 (1.0 atm), methanol (1.0 mL), r. t., 18 h. 2 Turnover number (TON) = mmol of product/mmol of total metal except Fe. 3 Determined from 1H NMR spectral analysis through the use of mesitylene as an internal standard. 4 N. D. = not detected. 5 Pd–Fe3O4 (2.8 mol%) was used as a catalyst. 6 Au–Fe3O4 (2.8 mol%) was used as a catalyst. 7 An air balloon was used instead of O2. 8 An average value of three runs (91%, 90%, and 88%). 9 Result with 1a (0.50 mmol) in MeOH (2.0 mL). 10 Yield of isolated product. 11 Result with 1a (1.0 mmol) in MeOH (1.0 mL), 4 h. 12 Ethanol (1.0 mL) was used instead of methanol. 13 Yield of 2a’. 14 Result with 0.40 mol% of catalyst.