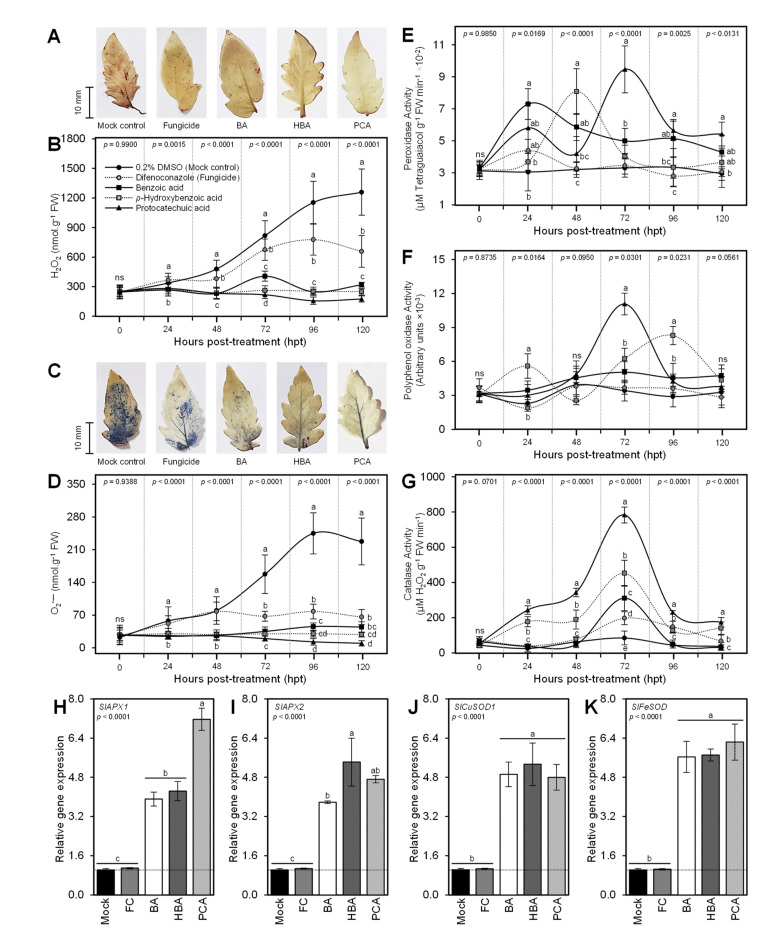
Figure 7.
Benzoic acid (BA) and its hydroxylated derivatives, ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid (HBA) and protocatechuic acid (PCA), alleviate oxidative stress and enhance the antioxidant defense-related enzymes in Alternaria solani-infected leaves under greenhouse conditions. (A) In situ histochemical localization of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) using DAB-based staining at 72 hpt with BA or one of its hydroxylated derivatives, (B) H2O2 content (nmol g−1 FW) after the treatment with BA or one of its hydroxylated derivatives, (C) in situ histochemical visualization of superoxide anion (O2•−) using NBT-based staining at 72 hpt with BA or one of its hydroxylated derivatives, (D) O2•− content (nmol g−1 FW) after the treatment with BA or one of its hydroxylated derivatives, (E) peroxidase activity (μM Tetraguaiacol g−1 FW min−1), (F) polyphenol oxidase activity (Arbitrary units), and (G) catalase activity (μM H2O2 g−1 FW min−1). Values represent the means of six biological replicates (n = 6), while whiskers reflect the standard deviation (means ± SD). (H–K) Relative gene expression of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 1 (SlAPX1), cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 2 (SlAPX2), superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] 1 (SlCuSOD1), and iron superoxide dismutase (SlFeSOD), respectively. Values represent the means ± standard deviation (means ± SD) of five biological replicates (n = 5). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05). Mock: 0.2% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated (mock control), FC: difenoconazole-treated (fungicide), BA: benzoic acid-treated, HBA: ρ-hydroxybenzoic acid-treated, and PCA: protocatechuic acid-treated.